Are you looking to increase the voltage or amp-hour capacity of your battery system? Understanding how to connect batteries in series or parallel can help you achieve your desired power output. Whether you are working with lead acid or lithium batteries, knowing the right configurations is essential for optimizing performance. Let’s explore the steps involved in connecting batteries in series or parallel to enhance your power capabilities.
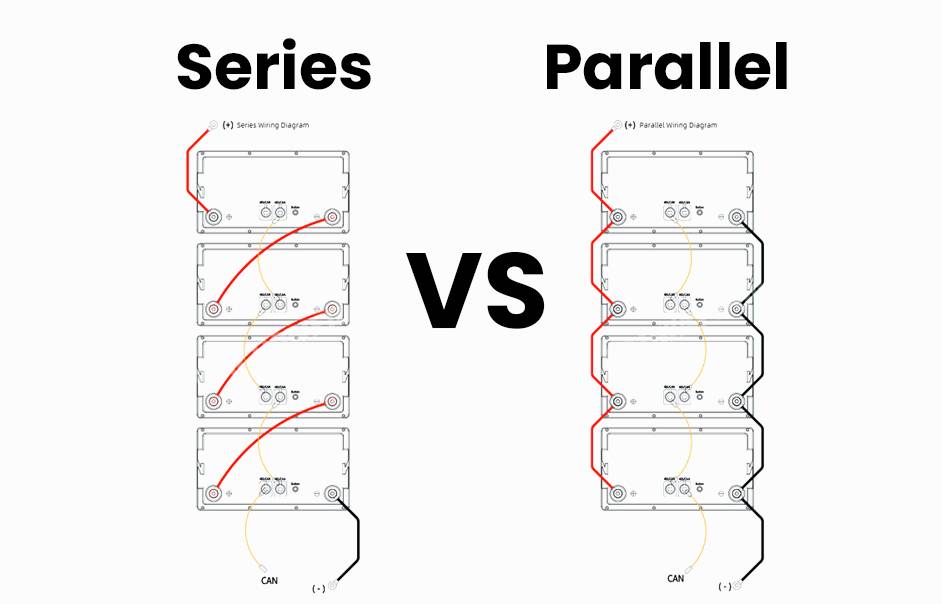
Connecting Batteries in Series
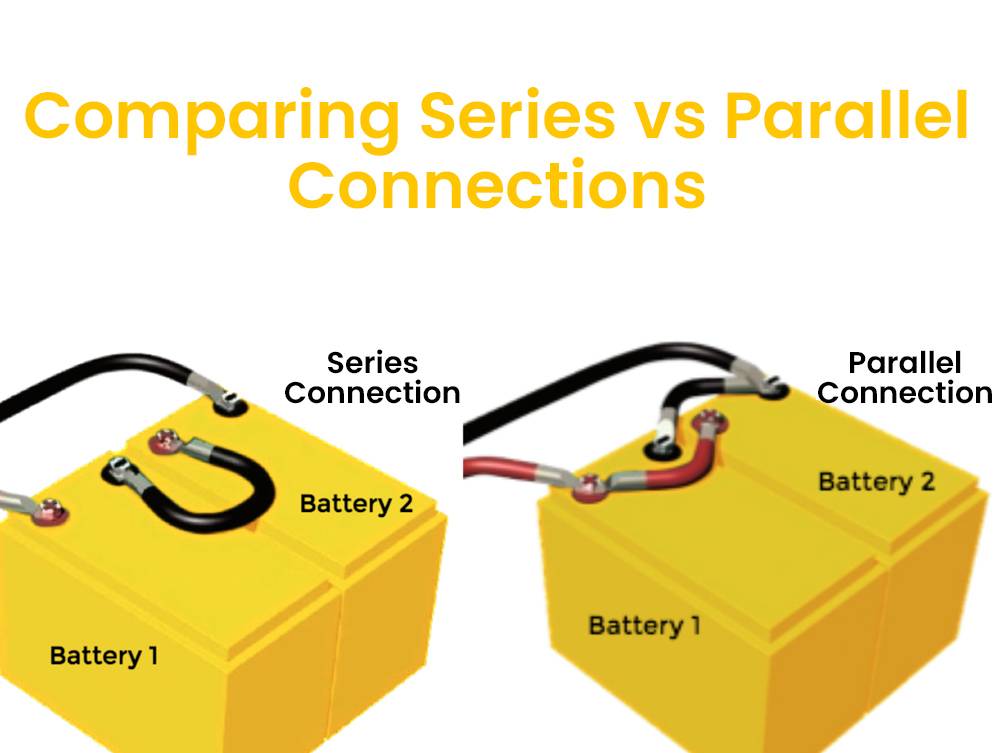
To connect batteries in series, you connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of another, and so on, until all batteries are connected. This increases the total voltage of the battery bank. Connecting batteries in series is useful when you need higher voltage for your application, such as in electric vehicles or solar power systems.
- Ensure that all batteries have the same voltage and capacity rating to prevent damage.
- Connect the negative terminal of one battery to the positive terminal of another, repeating this process for all batteries in the series.
- Attach a cable from the negative terminal of the first battery to your application, and another cable from the positive terminal of the last battery to your application.
- Use a charger that matches the battery system voltage when charging batteries in series to avoid imbalance.
Connecting Batteries in Parallel
When connecting batteries in parallel, the positive terminals of all batteries are connected together, and the negative terminals are connected together. This configuration allows the total voltage of the batteries to remain the same while adding their currents together. Connecting batteries in parallel is useful when you need to increase the available current for your application.
To connect batteries in parallel:
- Ensure that all batteries have the same voltage and ideally the same capacity.
- Connect the negative terminals of all batteries together and the positive terminals together.
- For example, to create a 12V 400Ah battery system, connect four 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel.
- Charging parallel connected batteries may take longer, but you can safely reduce the charge time by increasing the charging current.

Series-Parallel Connected Batteries
Connecting batteries in series-parallel is a method where batteries are connected both in series and parallel to increase both the voltage and capacity of the battery system. For example, connecting batteries in series-parallel can be achieved by configuring multiple strings of batteries to increase both voltage and capacity.
Series-parallel connected batteries offer both increased voltage and capacity. This configuration involves connecting multiple sets of batteries in both series and parallel. For example, to create a 12V 300Ah battery system, you can connect six 6V 100Ah batteries in series and parallel.
It’s essential to consult with battery experts when configuring batteries in series, parallel, or series-parallel to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the principles of series and parallel connections can help you maximize the efficiency of your battery system for various applications.
If you’re considering lithium batteries wholesale or OEM, explore Redway Power, which allows for safe series or parallel connections, ideal for higher voltage or capacity requirements. Reach out to our experts for personalized guidance on configuring batteries for your specific needs.
FAQs
Is it better to connect batteries in series or parallel?
When connecting batteries, whether it is better to connect them in series or parallel depends on specific needs and requirements. Connecting batteries in series increases the total voltage, while connecting them in parallel increases the total current capacity. Series connections are suitable for applications that require higher voltage output, while parallel connections are ideal for applications that require increased current capacity.
How do you tell if 2 batteries are in series or parallel?
To determine if 2 batteries are connected in series or parallel, look for the connection between their positive and negative terminals. If the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the other, they are connected in series. If both positive terminals are connected together and both negative terminals are connected together, they are connected in parallel.
Can you put 2 12V batteries in series?
Yes, you can put 2 12V batteries in series to obtain a total voltage of 24V. To connect batteries in series, you connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the other. This configuration doubles the voltage while keeping the current the same.
Can you run 2 12V batteries in parallel?
Yes, you can connect 2 12V batteries in parallel. This involves connecting the positive terminal of one battery to the positive terminal of the other, and the negative terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the other. Connecting batteries in parallel increases the total capacity while maintaining the same voltage.
Can you mix 100Ah and 200Ah batteries?
It is not recommended to mix 100Ah and 200Ah batteries in the same battery bank. It is best to use batteries of the same capacity and type for optimal performance and longevity. Mixing different capacity batteries can lead to imbalances in charging and discharging, potentially reducing the overall efficiency and lifespan of the battery bank.
What happens if you put two batteries in parallel?
When you connect two batteries in parallel, the capacity of the battery bank increases, but the voltage remains the same. Batteries connected in parallel must have the same voltage rating. Connecting batteries in parallel is not recommended if the batteries are not identical in voltage and capacity.
What happens when you put two batteries in series?
When you put two batteries in series, their output voltages add up, resulting in a greater total voltage. For example, if you connect two 1.5V batteries in series, the total voltage will be 3.0V. However, it is important to note that when connecting batteries in series, the current remains the same, and the voltage across the circuit is the sum of the individual voltage drops across each battery.
How many 12-volt batteries can you run in parallel?
There is no limit to how many 12-volt batteries you can run in parallel. Connecting batteries in parallel increases the overall capacity and provides a longer runtime. However, it is important to ensure that all batteries in the parallel circuit have the same voltage rating. When connecting batteries in parallel, be cautious of the wiring and ensure proper cable sizing to avoid short circuits.
Can you put AA batteries in parallel?
It is generally not recommended to put AA batteries in parallel. Connecting batteries in parallel can lead to imbalances in voltage and capacity, which can result in reduced performance and potential risks. It is best to use batteries of the same type, voltage, and capacity for optimal results.