Welcome to the captivating world of voltage protection in Battery BMS! In this blog post, we unravel the importance, mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages of overvoltage and undervoltage protection. Join us as we dive into the realm of safeguarding your battery’s lifespan and performance. Get ready to explore the electrifying world of voltage protection in batteries!
Importance of Proper Voltage Protection
Proper voltage protection is the unsung hero of battery management systems. It serves as a shield, guarding your battery from potential damage caused by voltage fluctuations. Imagine a surge in voltage frying your expensive battery – not cool! Voltage protection ensures that your battery operates within safe limits, prolonging its lifespan and reliability.
Think of it as an invisible guardian constantly monitoring and regulating the flow of electricity to keep things running smoothly. Without proper voltage protection, your battery is vulnerable to overcharging or discharging, leading to decreased performance and potentially hazardous situations.
By implementing robust voltage protection measures, you’re investing in the longevity and efficiency of your battery system. It’s like giving your battery a suit of armor against unpredictable electrical anomalies. So, next time you power up your device, remember the importance of having proper voltage protection in place for uninterrupted functionality.
What is Overvoltage Protection in Battery BMS?
Overvoltage protection in Battery BMS is a crucial feature that safeguards your battery pack from excessive voltage levels. When the incoming voltage exceeds the preset threshold, this protection mechanism kicks in to prevent damage to the battery cells and components.
By constantly monitoring the voltage levels, overvoltage protection ensures that your battery operates within safe limits. It acts as a shield against power surges, faulty chargers, or other external factors that could lead to an overcharge situation.
This protective function works by quickly disconnecting the charging source or load when it detects a voltage spike beyond the set limit. This rapid response helps maintain the longevity and performance of your battery system.
Implementing overvoltage protection in your Battery BMS not only prolongs the lifespan of your batteries but also enhances safety during charging and discharging processes. Its proactive nature can save you from costly repairs or replacements down the line.
How Does Overvoltage Protection Work in Battery BMS?
Overvoltage protection in Battery Management Systems (BMS) is like a vigilant guardian, constantly monitoring the voltage levels to ensure they don’t exceed safe limits. When the BMS detects a potential overvoltage situation, it swiftly springs into action, activating protective measures to prevent damage to the battery cells.
One way overvoltage protection works is by using sensors that continuously measure the voltage of each cell within the battery pack. If any cell’s voltage surpasses the predetermined threshold, the BMS will trigger mechanisms such as disconnecting charging sources or diverting excess energy away from the cells.
By swiftly responding to overvoltage events, BMS helps prolong battery life and reduce safety risks associated with excessive voltage levels. This proactive approach not only safeguards against damage but also enhances overall system efficiency and reliability.
Advantages of Overvoltage Protection
Overvoltage protection in Battery Management Systems (BMS) offers several key advantages that are crucial for the overall health and safety of batteries. One significant advantage is the prevention of damage to the battery caused by excessive voltage levels, which can lead to overheating and even combustion. By cutting off power when overvoltage occurs, this feature helps prolong the lifespan of batteries, ensuring they operate efficiently for longer periods.
Additionally, overvoltage protection enhances user safety by reducing the risk of electrical hazards such as short circuits or fires resulting from voltage spikes. This feature provides peace of mind to users knowing that their batteries are equipped with safeguards against potential dangers.
Moreover, overvoltage protection can also improve overall system reliability by maintaining stable voltage levels within safe limits. This stability ensures consistent performance and prevents unexpected shutdowns due to voltage irregularities.
Incorporating overvoltage protection in Battery BMS not only safeguards battery health and longevity but also enhances user safety and system reliability.
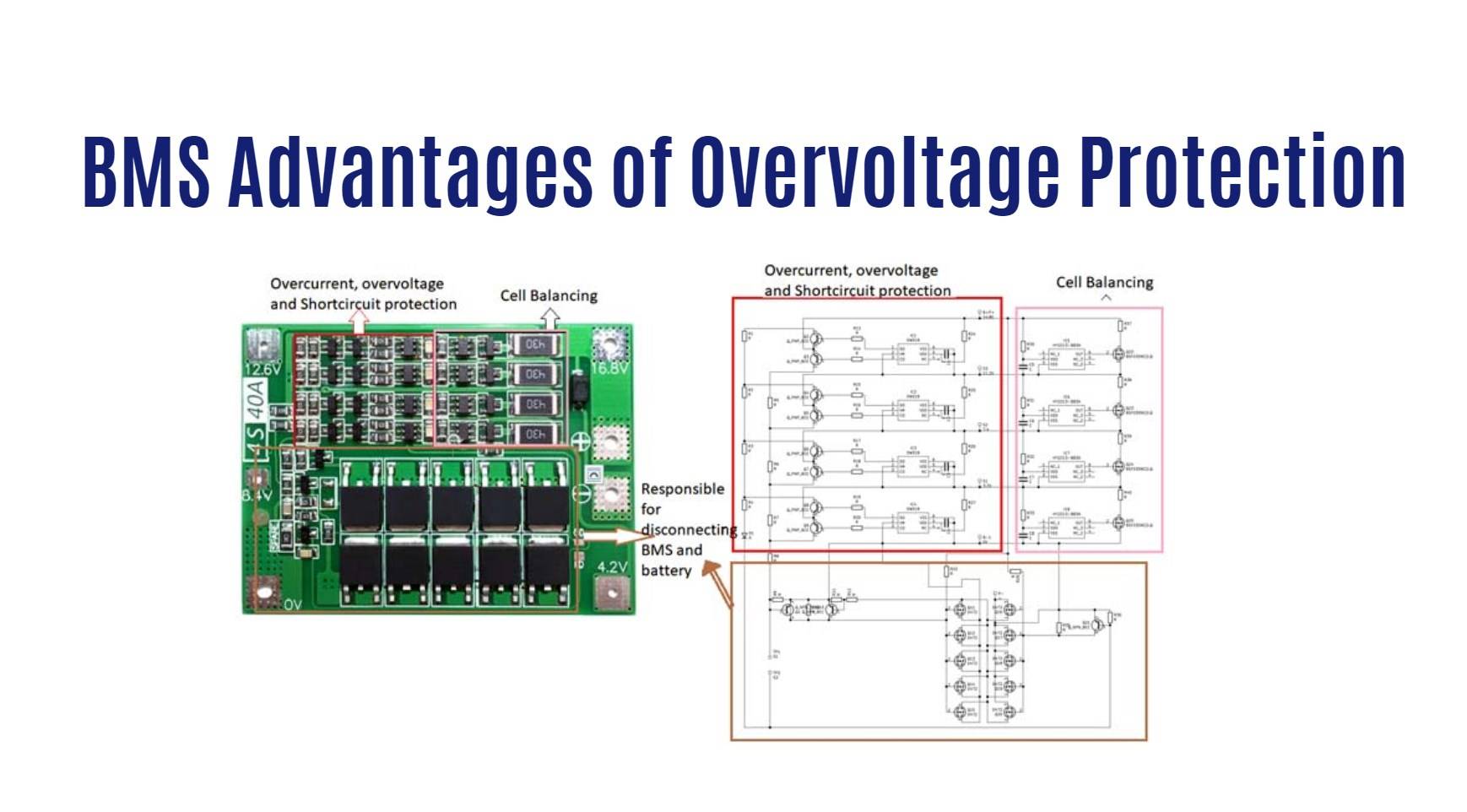
Disadvantages of Overvoltage Protection
While overvoltage protection is crucial for safeguarding battery systems, it does come with its own set of drawbacks. One disadvantage is the potential for false triggers, where the protection system might mistake a harmless voltage spike for a genuine threat. This can lead to unnecessary interruptions in power supply or even damage to the battery itself.
Another drawback is the added complexity and cost that comes with implementing overvoltage protection mechanisms in a Battery Management System (BMS). The need for additional components and circuitry can increase manufacturing expenses and make maintenance more challenging.
Moreover, overvoltage protection systems may introduce delays in response time, especially if they are overly sensitive. In critical applications where immediate power availability is paramount, any delay could be detrimental.
It’s essential to strike a balance between robust overvoltage protection and efficient operation to mitigate these disadvantages effectively.
What is Undervoltage Protection in Battery BMS?
Undervoltage protection in Battery Management Systems (BMS) is a crucial feature that safeguards batteries from operating at excessively low voltages. When the voltage drops below a certain threshold, undervoltage protection kicks in to prevent damage and potential safety hazards. This is especially important in applications where maintaining optimal battery performance is essential.
The way undervoltage protection works is by monitoring the battery’s voltage levels constantly. If it detects that the voltage has fallen below the set limit, it triggers protective measures to either alert the user or automatically disconnect the power source to prevent further discharge.
By providing undervoltage protection, BMS ensures longevity and reliability of batteries by preventing deep discharges that can degrade their lifespan. Additionally, this feature helps maintain stable performance and prevents unexpected shutdowns due to insufficient voltage levels.
However, relying solely on undervoltage protection may not address all potential issues related to battery health and performance. It’s important to consider other factors such as overcurrent protection and temperature management for comprehensive battery care.
How Does Undervoltage Protection Work in Battery BMS?
Undervoltage protection in a Battery Management System (BMS) is crucial for ensuring the battery operates within safe parameters. When the battery voltage drops below a preset threshold, the BMS triggers protective measures to prevent damage.
The BMS constantly monitors the battery voltage levels through sensors and compares them to predefined thresholds. If the voltage falls below the set limit, it sends signals to disconnect power flow or trigger an alarm.
This protection mechanism safeguards the battery from being over-discharged, which can lead to decreased performance or even permanent damage. Undervoltage protection helps extend the lifespan of batteries by preventing harmful deep discharges that can shorten their operational life.
By implementing undervoltage protection in a BMS, users can have peace of mind knowing that their batteries are being safeguarded against potentially damaging scenarios.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Undervoltage Protection
Undervoltage protection in Battery Management Systems (BMS) offers several benefits. One advantage is that it helps prevent damage to the battery by ensuring it doesn’t operate at voltage levels that are too low, which can lead to performance issues or even failure. This feature also prolongs the overall lifespan of the battery by maintaining optimal operating conditions.
On the downside, undervoltage protection can sometimes be overly sensitive, triggering unnecessary shutdowns when voltage levels fluctuate slightly below the set threshold. This could potentially disrupt operations and cause inconvenience for users who rely on continuous power supply.
Despite its drawbacks, undervoltage protection remains a crucial aspect of BMS functionality, providing essential safeguards against potential risks associated with low voltage scenarios. By striking a balance between sensitivity and reliability, manufacturers continue to refine this feature to enhance overall battery performance and safety.
Disadvantages of Undervoltage Protection
Undervoltage protection in battery BMS, while essential, comes with its own set of disadvantages. One drawback is that it can lead to premature battery depletion if not calibrated correctly. This could result in reduced battery life and overall performance.
Additionally, undervoltage protection may trigger false alarms if the voltage thresholds are set too sensitively. This can be frustrating for users and may cause unnecessary disruptions in power supply.
Moreover, relying solely on undervoltage protection without proper monitoring of other parameters like temperature or current flow could leave the system vulnerable to potential damage or failures.
It’s important to weigh these drawbacks against the benefits of undervoltage protection to ensure a well-balanced and efficient battery management system.
Comparison between Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
When it comes to protecting your battery, both overvoltage and undervoltage protection play crucial roles in ensuring its longevity and safety.
Overvoltage protection safeguards the battery from excessive voltage levels that could lead to damage or even catastrophic failure. It acts as a shield against potential hazards caused by spikes in voltage, providing peace of mind for users.
On the other hand, undervoltage protection prevents the battery from being drained beyond safe levels, prolonging its lifespan and performance. By monitoring and maintaining the minimum voltage threshold, undervoltage protection ensures optimal functionality of the battery.
A comprehensive Battery Management System (BMS) should ideally incorporate both overvoltage and undervoltage protection mechanisms to provide complete safeguarding for your batteries. Choosing the right balance between these two protections will ultimately determine the efficiency and durability of your battery system.