- Forklift Lithium Battery
- Golf Cart Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
51.2V 100Ah Rackmount LiFePO4 Battery
8000 times (80% DOD 0.5C)
Optional SNMP for TELECOM - Car Starter Battery
- 12V LiFePO4 Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | Self-heating
LiFePO4 | Group 31
UL 1642 | IEC 62619 - 24V LiFePO4 Battery
- 36V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V LiFePO4 Battery
60V 100Ah Lithium Battery (AGV, AMR, LGV)
Peak Discharge Current 400A
500 x 298 x 349 mm - 72V~96V LiFePO4 Battery
72V 100Ah Lithium Golf Cart Battery
Peak Discharge Current 315A (10S)
740 × 320 × 246 mm - Wall-mounted Lithium Battery
51.2V 100Ah 5kWh
Wall-mounted Battery532 x 425 x 170 mm / LiFePO4
>8000 Cycles (80% DOD 0.5C)
RS485 / CAN-bus
for Solar Home ESS - Home-ESS All-in-One
51.2V 32kWh
All-in-On HESS SystemPowerAll
51.2V / LiFePO4
>8000 Cycles (80% DOD 0.5C)
RS485 / CAN-bus / WiFi
All-in-One for Home ESS
What You Need to Know About Lithium Battery Electrolytes
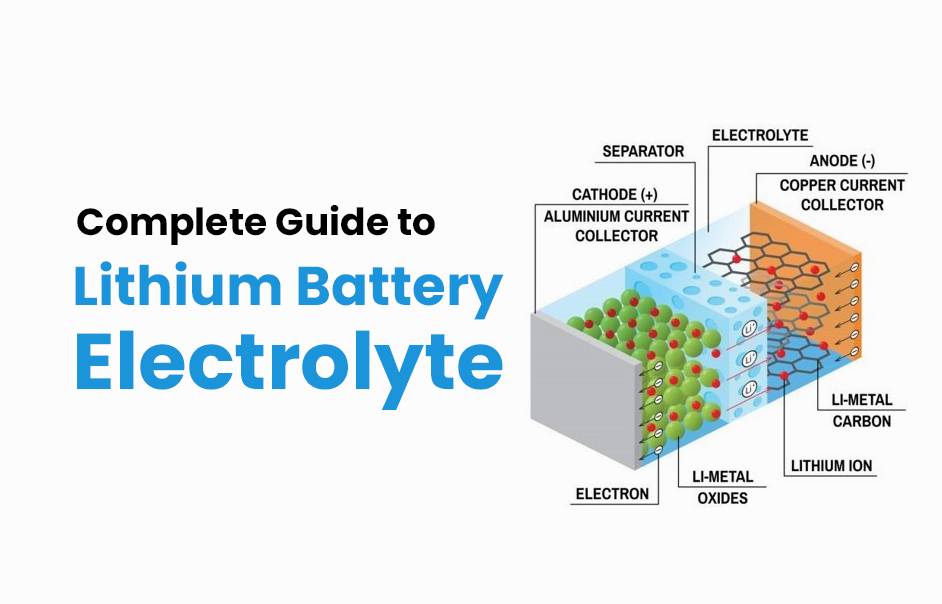
Lithium battery electrolytes enable the movement of lithium ions between electrodes, facilitating charge and discharge cycles in lithium-ion batteries. Composed mainly of lithium salts, organic solvents, and performance-enhancing additives, electrolytes critically influence battery voltage, capacity, safety, temperature tolerance, and cycle life. Innovations in electrolyte chemistry and form — liquid, gel, or solid-state — continue to revolutionize battery technology.
What is the role of electrolytes in lithium batteries?
Electrolytes serve as the ion-conducting medium between the positive cathode and negative anode of lithium batteries, allowing lithium ions to move during charge and discharge while being electronically insulating. They ensure electrical continuity via ionic conduction, influence battery voltage stability, and affect factors such as energy density, safety, and thermal management.
What are the main components of lithium battery electrolytes?
A typical lithium battery electrolyte consists of three main components:
- Solvents: Usually organic carbonates like ethylene carbonate (EC), propylene carbonate (PC), and linear carbonates (DMC, DEC, EMC), providing a stable chemical environment for lithium-ion migration.
- Lithium salts: Such as lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI), or lithium tetrafluoroborate (LiBF4), supplying mobile lithium ions and enabling charge transport.
- Additives: Chemical compounds improving electrolyte stability, enhancing safety by suppressing side reactions, aiding solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation, flame retardancy, and extending battery lifespan.
How do different types of lithium battery electrolytes compare?
- Liquid Electrolytes: The most common, consisting of dissolved lithium salts in organic solvents. They offer high ionic conductivity but are flammable and require careful management.
- Gel Electrolytes: Incorporate polymers to immobilize liquid electrolytes, reducing leakage and improving safety, with moderate ionic conductivity.
- Solid-State Electrolytes: Include polymer, ceramic, or glassy materials that eliminate liquid solvents, offering superior safety, higher energy densities, and wider temperature operability but face challenges in ionic conductivity and interface stability.
How do electrolytes affect lithium battery performance and safety?
Electrolyte chemistry directly impacts voltage stability, ionic conductivity, thermal stability, and resistance to degradation. Well-formulated electrolytes minimize side reactions that reduce capacity and cycle life. Stable electrolytes prevent thermal runaway by resisting decomposition at high temperatures, thereby enhancing safety. Additives help form protective layers on electrodes, improving overall battery durability.
What innovations are advancing lithium battery electrolytes?
Developments include non-flammable solvents, multifunctional additives that enhance low-temperature performance, and solid-state electrolytes enabling safer, higher-energy batteries. Research focuses on reducing harmful decomposition products like HF, optimizing SEI formation, and increasing electrolyte stability over hundreds to thousands of cycles.
What environmental and manufacturing considerations relate to lithium battery electrolytes?
Electrolyte production involves organic solvents and lithium salts with environmental concerns regarding toxicity and disposal. Manufacturers like Redway Power invest in ISO 9001:2015-certified processes and advanced MES to ensure electrolyte purity, consistency, and safe integration into batteries, reducing waste and enhancing product reliability.
Comparison Chart: Key Properties of Lithium Battery Electrolyte Types
| Electrolyte Type | Ionic Conductivity | Safety Profile | Stability Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid | High | Moderate (flammable) | -20°C to 60°C | Consumer electronics, EV batteries |
| Gel | Moderate | Improved (less leakage) | -30°C to 70°C | Flexible batteries, medical devices |
| Solid-state | Lower (improving) | High (non-flammable) | -40°C to 120°C+ | Next-gen EVs, aerospace, grid storage |
Redway Power Expert Views
“Electrolytes are fundamental to unlocking lithium battery potential, balancing ion mobility with chemical stability to enable longer-lasting, safer batteries. At Redway Power, our commitment to ISO-certified quality and cutting-edge MES manufacturing ensures electrolytes meet the highest standards for OEM customers. This dedication allows us to deliver batteries that power innovations in energy density, safety, and sustainability across diverse industries.” – Redway Power Expert
Conclusion
Lithium battery electrolytes are critical to battery functionality, safety, and longevity, comprising solvents, lithium salts, and additives. Advances in electrolyte chemistry and forms—from liquid to solid-state—address challenges in conductivity, thermal stability, and environmental impact. Trusted manufacturers like Redway Power integrate rigorous quality controls and innovative materials to produce electrolytes that lead the evolution of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and beyond.
FAQs
What are the main components of lithium battery electrolytes?
Organic solvents, lithium salts, and functional additives.
Why is electrolyte stability important?
It prevents battery degradation, enhances safety, and extends lifespan.
Are solid-state electrolytes safer than liquid ones?
Yes, they eliminate flammable solvents and improve thermal stability.
How do additives improve lithium battery electrolytes?
They enhance conductivity, form protective layers on electrodes, and improve cycle life.
How does Redway Power ensure the quality of lithium battery electrolytes?
Through ISO 9001:2015 certification, MES-based manufacturing, and advanced material control.




























