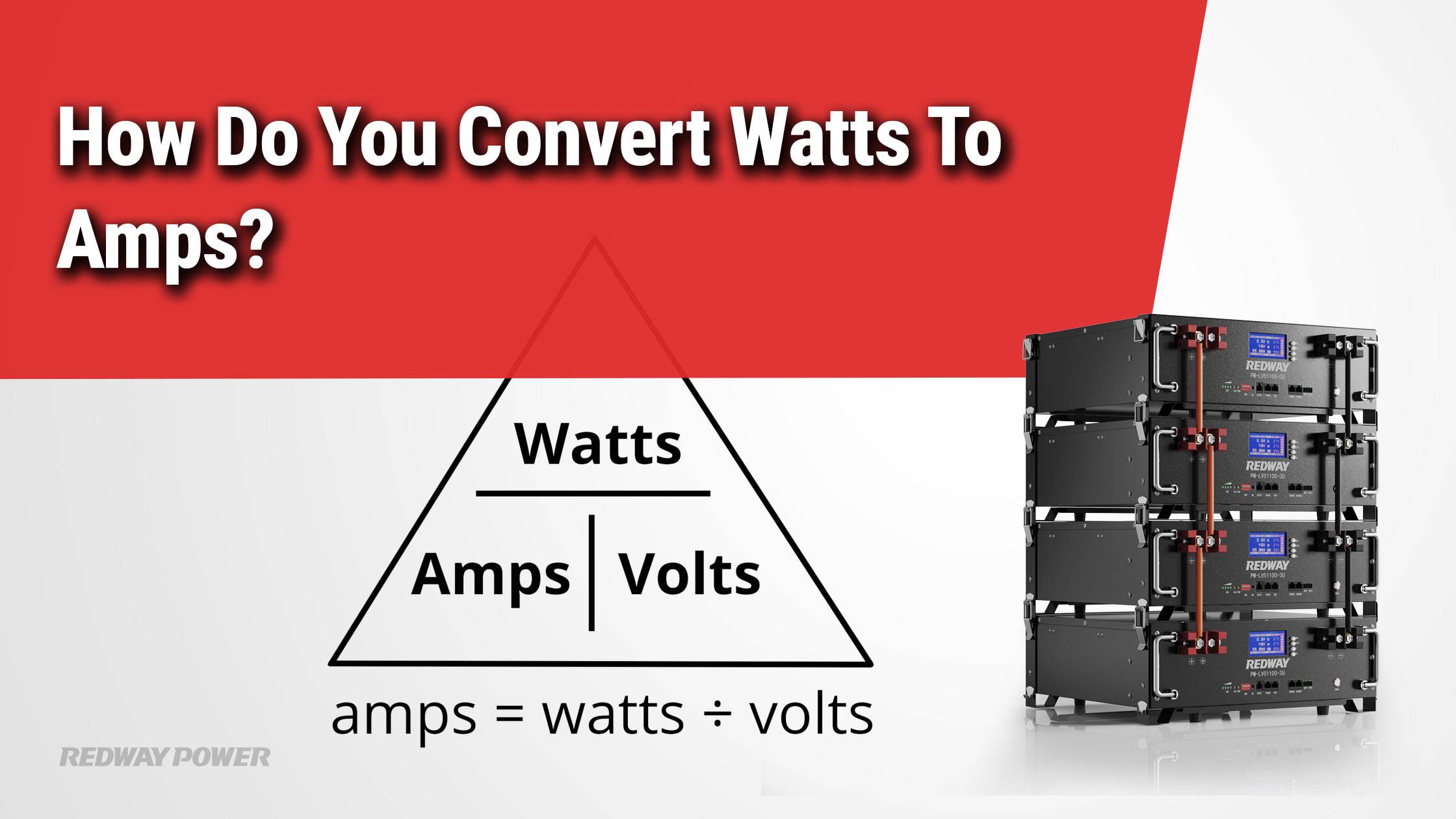
When converting watts to amps, remember Watt’s Law: Amps = Watts ÷ Volts. Imagine it as sharing the power among the voltage to find the current. For example, a 1000W appliance on a 240V circuit draws 4.17 amps. Remember, these points are easy to grasp — like explaining to a friend how to bake the perfect cookie!
Understanding the relationship between watts and amps
Watts and amps work together in electrical systems. Amps (current) flow like water in a river, while watts (power) combine amps and voltage. Remember: watts = amps × volts—it’s the secret sauce!
Understanding watts and amps might seem like deciphering a secret recipe. But fear not! Let’s break it down into simple ingredients and steps. Next time you flip a switch, remember: watts and amps work together, creating the magic of electricity. It’s like serving up a fresh, electrifying dish!
The formula for converting watts to amps
Understanding watts and amps is like decoding an electric recipe. Amps (current) flow like water in a river, while watts (power) combine amps and voltage. Remember: watts = amps × volts—it’s the secret sauce!
Electricity — our invisible helper! But how do watts and amps dance together? Let’s demystify it.
- Amps Flow Like Rivers:
- Current (Amps): Picture a river—the flow of electrons. Amps measure this flow. More amps, faster current!
- Voltage (Volts): Voltage is like the river’s slope—it pushes electrons. Higher volts, steeper slope!
- Watts: The Electric Recipe:
- Ingredients: Combine amps and volts. Imagine it as the force pushing those electrons—the power supply.
- Formula: Watts = Amps × Volts. It’s like mixing flour (amps) and sugar (volts) for a tasty treat.
- Conclusion:
- Next time you flip a switch, remember: watts and amps make the magic happen. Electricity, served fresh!
Remember, these points are easy to grasp—like explaining to a friend how to make a sandwich!
Examples of converting watts to amps
When it comes to converting watts to amps, it can be helpful to see some examples in action. Let’s take a look at a few scenarios where we need to convert watts into amps.
Example 1:
Imagine you have a device that consumes 500 watts of power. To find the amperage, you can use the formula P = VI (power equals voltage multiplied by current). Let’s say the voltage is 120 volts. By rearranging the formula, we get I = P/V. Plugging in the values, we get I = 500/120 ≈ 4.17 amps.
Example 2:
Now let’s consider an appliance with a power rating of 1500 watts and a voltage of 240 volts. Using the same formula as before, I = P/V, we find that I = 1500/240 ≈ 6.25 amps.
Example 3:
To illustrate another scenario, let’s say you want to determine how many amps are needed for a string of LED lights that consume only15 watts with a voltage supply of12 volts. Applying our trusty formula once again gives us I = P/V: I=15/12 ≈1.25amp
These examples demonstrate how using the simple equation P=VI allows us to convert wattage into amperage based on specific electrical parameters.
Common misconceptions about watts and amps
Common misconceptions about watts and amps include interchanging voltage and current ratings for devices, misconceptions about the relationship between watts and volume in amplifiers, and confusion between amps and volts. Understanding these misconceptions helps clarify the correct usage and interpretation of electrical units.
Common misconceptions about watts and amps can lead to misunderstandings about electrical units and their applications. It is important to address these misconceptions to ensure accurate understanding and usage of electrical measurements.
- Interchanging Voltage and Current Ratings: One common misconception is interchanging voltage and current ratings for devices, which can lead to incorrect usage and potential device damage.
- Relationship between Watts and Volume: Another misconception is assuming a direct relationship between watts and volume in amplifiers, when other factors such as speaker efficiency and design also play a role.
- Confusion between Amps and Volts: Amps and volts are different electrical units, with amps representing current flow and volts representing electrical potential. Understanding this distinction is crucial for proper electrical system understanding.
By addressing common misconceptions about watts and amps, we can improve our understanding and usage of electrical units. Clarifying the interchanging of voltage and current ratings, the relationship between watts and volume, and the distinction between amps and volts helps ensure accurate interpretation and application of electrical measurements.
Practical applications for converting watts to amps
A practical application of converting watts to amps is understanding the current drawn by electrical devices. By dividing the wattage of a device by the voltage it operates on, you can determine the current it draws in amps. This conversion is useful for power consumption analysis, selecting appropriate electrical components, and ensuring compatibility between devices and power sources.
Converting watts to amps has practical applications in understanding power consumption, selecting electrical components, and ensuring device compatibility. By dividing the wattage of a device by its operating voltage, one can determine the current drawn in amps, providing valuable insights into electrical systems.
- Current Determination: Converting watts to amps allows for the determination of the current drawn by electrical devices.
- Power Consumption Analysis: Understanding the current drawn helps in analyzing power consumption and managing electrical loads effectively.
- Component Selection: Converting watts to amps assists in selecting the appropriate electrical components based on current requirements and system specifications.
By converting watts to amps, one can gain insights into power consumption, select suitable electrical components, and ensure compatibility between devices and power sources. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions and optimize the performance of their electrical systems.
Post Views: 84