Understanding the Basics: Ah and Watts
Understanding Ah (ampere-hours) and Watts is essential in the world of electrical systems. Ah measures a battery’s capacity, akin to a fuel tank size, while Watts represent the speed of energy consumption.

- Ah and Watts Fundamentals:
- Ah: It measures a battery’s total charge over time, like a fuel tank’s capacity.
- Watts: Represents how quickly energy is used or consumed.
- Analogy for Clarity:
- Imagine a car with a 10-gallon fuel tank (Ah) driving at 60 mph (Watts). Larger tank (Ah) means longer drive time, while higher speed (Watts) implies quicker energy consumption.
- Real-world Significance:
- Knowing Ah and Watts helps estimate battery life for various devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles.
- Critical for comparing batteries for applications like backup power systems or cordless drills.
- Conversion Importance:
- While Ah indicates capacity, it doesn’t reveal how quickly a device drains a battery.
- Converting Ah to Watts becomes valuable for accurate understanding of power usage.
- Practical Applications:
- Crucial in determining battery duration for powering different devices in real-life scenarios.
- Essential for comparing batteries based on Ah and Watt-hours for specific applications.
Conclusion: Understanding the relationship between Ah and Watts empowers users to make informed decisions regarding battery usage, ensuring optimal performance in a variety of electrical applications.
The Relationship Between Ah and Watts
Understanding the relationship between Ah (ampere-hour) and Watts is essential for gauging power capacity and usage in devices or batteries. While Ah measures charge capacity, Watts represent the rate of energy consumption.
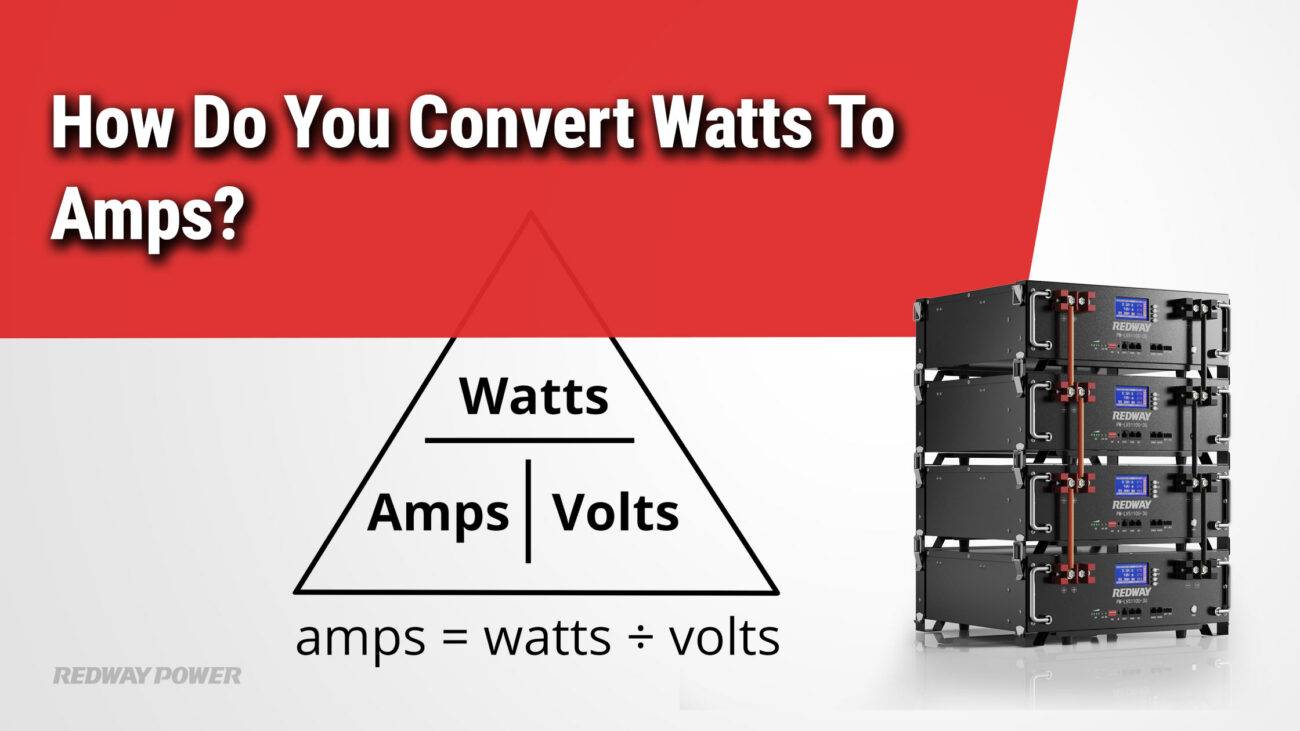
- Formula for Relationship:
- Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) x Current (Amps): This formula highlights that both voltage and current are needed to calculate power in watts. Ah alone doesn’t directly convert to watts.
- Practical Example:
- Take a 12V battery with 100Ah capacity. To find watts, multiply voltage by ampere-hour: 12V x 100Ah = 1200W. This reveals the power output potential before recharging.
- Application in Real Life:
- Essential for sizing batteries in solar systems or selecting backup power solutions.
- Accurate Ah to Watts conversion ensures devices receive sufficient power without system overload.
- Consideration of Efficiency:
- Efficiency Losses: Factors like DC to AC conversion losses may slightly affect accuracy but are typically negligible.
- Important to account for these factors in conversions for precise application-specific results.
- Manufacturer Specifications:
- Check Specifications: To ensure accuracy, refer to manufacturer specifications for devices or batteries involved in calculations.
- These specifications provide crucial information on voltages and currents for precise Ah to Watts conversions.
Converting Ah to Watts: Step by Step Guide
Understanding how to convert Ah (Ampere-hour) to Watts is crucial for managing electrical systems. Follow this step-by-step guide for accurate conversions between these two important units.

- Determine the Voltage:
- Find Voltage: Check the label or specifications of your battery or device to identify the voltage in Volts. This is the starting point for the conversion.
- Calculate Watt-Hours:
- Multiply Ah by Voltage: Multiply the Ah rating by the voltage to get watt-hours (Wh). For example, a 10Ah battery with a voltage of 12V results in 120Wh.
- Convert Watt-Hours to Watts:
- Divide by Time: To get watts, divide the watt-hour value by time (in hours). For instance, if you have 120Wh and want to know the watts consumed in one hour, the result is 120W.
- Consider Real-world Factors:
- Efficiency and Power Fluctuations: Keep in mind that this formula assumes constant power usage over time. Real-world scenarios may vary due to efficiency losses and fluctuations in power consumption.
By following these straightforward steps, you can accurately convert Ah to Watts, providing better insights for managing your electrical systems.
Practical Applications of Converting Ah to Watts
Now that you’ve mastered the conversion from Ampere-hours (Ah) to Watts, let’s explore the practical applications that make this conversion a valuable tool.
- Battery Capacity Calculation:
- Essential Insight: For those working with batteries, converting Ah to Watts is crucial for estimating energy capacity accurately. It helps determine how long batteries will last in various applications.
- Solar Power Systems:
- Matching Energy Demands: When dealing with solar power systems, converting Ah ratings to watts ensures the battery bank aligns with the system’s energy needs. This is vital for effective design and maintenance.
- Electric Vehicles:
- Charging and Range Planning: In the realm of electric vehicles, converting Ah to Watts is significant for charging system understanding and range calculations. It aids in planning trips and assessing charging requirements accurately.
- Off-Grid Power Solutions:
- Accurate Sizing: Whether setting up an off-grid cabin or powering remote equipment, converting Ah to Watts enables precise sizing and selection of batteries and solar panels based on expected usage patterns.
- Electronics Design:
- Insights for Efficiency: For electronic enthusiasts or engineers designing battery-powered circuits or devices, converting ampere-hour ratings to wattage provides insights into power requirements. This knowledge is essential for optimizing efficiency in electronic designs.
By applying these conversions in real-life scenarios, individuals can make informed decisions about their power needs, ensuring efficiency and reliability in various applications.
Factors That Affect the Conversion
When converting Ah to Watts, several factors can influence the accuracy of your calculations. It’s crucial to be aware of these factors to ensure reliable results tailored to your specific device or system.

- Efficiency of the Device or System:
- Varied Efficiency Levels: Devices have different efficiency levels, affecting the energy required for tasks. Understanding your device’s efficiency rating is essential for precise conversions from Ah to Watts.
- Voltage Level:
- Direct Proportional Impact: Voltage and power have a direct proportional relationship. Adjust calculations accordingly when dealing with high-voltage systems to maintain accuracy in Ah to Watts conversions.
- Additional Components or Accessories:
- Impact on Power Consumption: Connected components or accessories can influence overall power consumption, thus affecting the conversion from Ah to Watts. Consider these elements for more accurate results.
- Temperature Influence:
- Variable Battery Performance: Temperature variations affect battery performance, impacting capacity and discharge rates. Be mindful of temperature changes as they can influence the accuracy of conversions.
- Battery Degradation Over Time:
- Gradual Capacity Diminishment: Batteries degrade with time, affecting their capacity and efficiency. This degradation should be considered when converting Ah units into Watts for more realistic results.
By taking these factors into account during conversions, you ensure precision in your results, tailored to the specific conditions of your device or system.
Tips for Accurate Conversions
Converting Ah to Watts may seem complex, but with a grasp of the basics and adherence to specific guidelines, accurate calculations become straightforward. Here are essential tips to ensure precision in your conversions:
- Double-Check Units:
- Unit Accuracy: Verify correct units for both Ah and Watts before starting the conversion. Mixing up units can lead to inaccuracies in results.
- Use Reliable Formulas:
- Appropriate Formulas: Utilize specific formulas based on factors like voltage and time. Ensure the chosen formula aligns with your specific scenario for accurate conversions.
- Consider Efficiency Losses:
- Account for Inefficiencies: Acknowledge that no system is 100% efficient. Factor in energy losses during conversions or inefficiencies in equipment when calculating Wattage from Ampere-hours.
- Factor in Discharge Rates:
- Consider Device Dynamics: For batteries or energy storage devices, account for discharge rates. This factor influences how quickly they deliver power over time.
- Consult Manufacturer Specifications:
- Reliable Device Information: When dealing with specific appliances, refer to manufacturer specifications for accurate data on power consumption or battery capacity ratings.
- Recalculate Periodically:
- Adapt to Changes: Recognize that battery performance changes over time due to aging and usage. Periodically reassess your conversions, particularly when batteries are used as a power source.
By incorporating these tips, you’ll confidently convert Ah to Watts, aligning your power requirements accurately. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast or optimizing power usage, mastering this skill enhances your understanding of energy measurements.