Embark on an enlightening journey into the world of batteries with our guide comparing lithium polymer and lithium-ion batteries. Known for high energy density, these essential power sources have distinct pros and cons. This guide empowers you to make informed decisions for your devices, exploring differences and applications. Join us for an electrifying exploration into the dynamic realm of battery technology – grab your favorite beverage and dive in!
Lithium Polymer vs Lithium ion Battery, What Are the Differences?
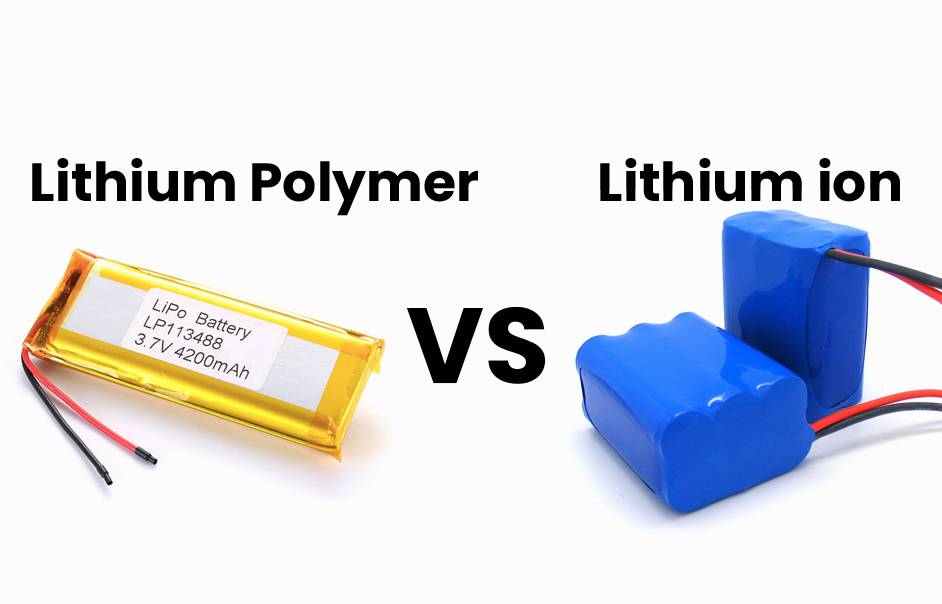
Navigating the world of batteries leads us to the choice between Lithium Polymer (LiPo) and Lithium Ion (Li-ion) batteries, both part of the lithium family. Delving into their differences is crucial for selecting the right power source for our devices.
- Construction:
- LiPo Batteries: Featuring a flexible polymer electrolyte, LiPos boast a thinner and lighter design, enhancing their suitability for compact devices like smartphones and wearables.
- Li-ion Batteries: Utilizing a liquid electrolyte housed in a rigid casing, Li-ion batteries offer a different structural approach.
- Energy Density and Shape Flexibility:
- LiPo Advantage: LiPos generally exhibit higher energy density, allowing them to store more power in a confined space, making them ideal for devices with size constraints.
- Charging Capabilities and Safety:
- Charging Speed: LiPos tend to charge faster than Li-ions due to lower internal resistance, but this comes with the risk of overheating if not handled with care.
- Safety Concerns: Both require careful handling and monitoring to avoid potential hazards like damage from overcharging or puncture, leading to fire risks.
While LiPo batteries excel in weight and size, catering to portable devices with high power demands, their safety concerns related to overheating should be noted. Li-ion batteries, offering longer overall lifespan, may be preferable for applications prioritizing safety over ultra-compact designs. Carefully weighing these factors ensures the right battery choice aligned with device requirements and safety precautions.
Pros and Cons of Lithium Polymer Batteries
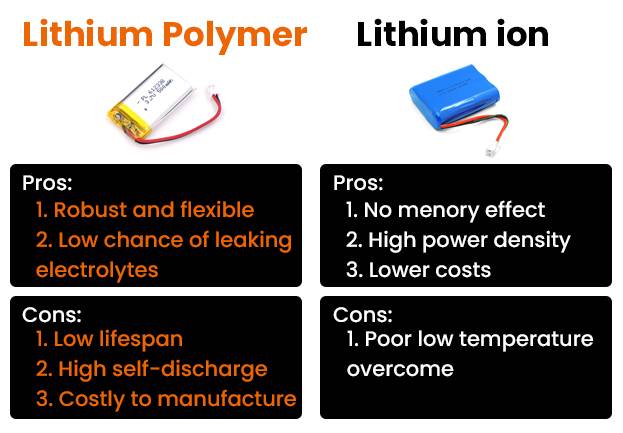
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries have become popular for their lightweight and flexible design, catering to the demands of modern portable devices. Let’s explore the pros and cons associated with these batteries.
- High Energy Density:
- Pro: LiPo batteries boast high energy density, allowing them to store a significant amount of energy in a compact size.
- Application: Ideal for portable devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearables where space is a crucial factor.
- Flexibility in Design:
- Pro: LiPo batteries can be molded into various shapes and sizes, offering flexibility in design for sleek and compact electronic devices.
- Contrast: Unlike traditional cylindrical lithium-ion batteries, LiPos provide manufacturers with design versatility.
- Low Self-Discharge and High Discharge Rate:
- Pro: LiPo batteries exhibit a lower self-discharge rate, retaining charge for longer durations during periods of inactivity.
- Pro: Higher discharge rates enable quick delivery of power when demanded by the device.
- Temperature Sensitivity and Special Handling:
- Con: LiPo batteries are sensitive to high temperatures, posing a risk of thermal runaway or rare instances of explosion.
- Handling Requirement: Special care is needed during charging and storage, requiring specific chargers and never leaving them unattended while charging.
While Lithium Polymer batteries offer notable advantages such as high energy density and design flexibility, it’s crucial to acknowledge their sensitivity to high temperatures and the necessity for proper handling during charging. Understanding these factors is vital in determining the suitability of LiPo batteries for your specific device or application.
Pros and Cons of Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have surged in popularity, driven by their high energy density and extended lifespan. Let’s delve into the pros and cons associated with these batteries.
- Compact and Lightweight:
- Pro: Lithium-ion batteries are known for their compact size and lightweight nature.
- Application: Ideal for powering portable electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets, allowing for greater design flexibility.
- High Energy Density:
- Pro: Lithium-ion batteries exhibit high energy density, storing a significant amount of energy relative to their size.
- Benefit: Enables devices to operate for extended periods without frequent recharging.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate:
- Pro: Lithium-ion batteries have a relatively low self-discharge rate, making them convenient for intermittent or backup power needs.
- Convenience: Retains charge for extended periods when not in use.
- Safety Concerns and Lifespan:
- Con: Safety is a major concern as lithium-ion batteries can overheat or catch fire in rare cases, emphasizing the need for careful handling.
- Con: Despite a long lifespan compared to other rechargeable batteries, lithium-ion batteries degrade over time and require eventual replacement.
- Cost Consideration:
- Note: While the initial cost of lithium-ion batteries may be higher, advancements in technology have been contributing to a decreasing cost over time.
Lithium-ion batteries offer compact size, high energy density, and a relatively low self-discharge rate, making them ideal for numerous applications. However, careful handling is essential due to safety concerns, and users should be prepared for eventual replacement as the battery degrades over its lifespan.
Which Battery Is Best for Your Device?
Selecting the right battery for your device involves considering crucial factors. This guide explores key considerations between lithium polymer (LiPo) and lithium ion (Li-ion) batteries.
- Size and Weight:
- LiPo Advantage: LiPo batteries excel in versatility, being lightweight and available in various shapes, ideal for devices with space or weight constraints.
- Li-ion Advantage: Li-ion batteries may be bulkier but offer higher energy density, providing more extended power for high-performance devices like smartphones or laptops.
- Power Output:
- Li-ion Advantage: With higher energy density, Li-ion batteries deliver more power for longer durations, catering to devices demanding sustained high performance.
- Design Flexibility:
- LiPo Advantage: LiPo batteries stand out for design flexibility, molding into different shapes, enabling manufacturers to create sleeker and slimmer devices.
- Safety Considerations:
- Safety Focus: Both batteries are generally safe, but Li-ion batteries carry a known risk of thermal runaway, potentially leading to overheating or fire. LiPo batteries, with a solid-state electrolyte, have a lower risk of thermal runaway.
The choice between LiPo and Li-ion hinges on specific needs. LiPo suits those prioritizing design flexibility and lightweight options, while Li-ion excels in delivering sustained high power. Consider size, power output, design flexibility, and safety when determining the best battery for your device.

Safety Considerations for Both Batteries
When selecting a battery for your device, safety should always be a top concern. Both lithium polymer and lithium ion batteries have unique safety considerations that users must be aware of.
- Lithium polymer batteries are lightweight and flexible but can swell or catch fire if mishandled. Avoid damaging the battery to prevent thermal runaway reactions.
- Lithium ion batteries are generally more stable than lithium polymer batteries but can still pose risks if misused. Overcharging or exposure to extreme temperatures can lead to internal damage and potential overheating or explosion.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines and use chargers designed for your battery type to ensure safe charging. Avoid leaving devices charging overnight or unattended.
- Store batteries in cool, dry places to minimize hazards. During transportation, secure batteries in protective cases or packaging.
By understanding and adhering to these safety precautions, users can enjoy the benefits of lithium polymer and lithium ion batteries without compromising safety. Remember to prioritize safety at all times.
Which one is safer, Lithium-Ion or Lithium Polymer batteries?
When comparing the safety of Lithium-Ion and Lithium Polymer batteries, it can be noted that Lithium Polymer batteries are considered safer than Lithium-Ion batteries due to various factors. Lithium Polymer batteries, an enhanced version of Lithium-Ion batteries, feature an aluminum casing that reduces the risk of explosions, hence making them a safer option.
Additionally, the absence of a liquid electrolyte in Lithium Polymer batteries minimizes the potential for leakage issues, further enhancing their safety profile. Overall, the design elements of Lithium Polymer batteries contribute to their improved safety features in comparison to traditional Lithium-Ion batteries.
How do Lithium Polymer Batteries operate?
Lithium Polymer batteries operate by utilizing a positive and negative electrode, as well as a dry solid, porous chemical, and gel-like electrolyte rather than a liquid one. This innovative design enables these batteries to offer distinct advantages, such as a lower profile, flexibility, and robustness.
Moreover, the absence of liquid electrolytes reduces the risk of leaks that could lead to thermal runaway, making Lithium Polymer batteries a safer option for various applications.
How do Lithium-Ion Batteries operate?
Lithium-ion batteries operate using a chemical composition that includes two positive and negative electrodes separated by a liquid chemical electrolyte. This composition limits them to a rectangular shape. These batteries have been in use since 1991 when Sony adopted them, and they are commonly used in portable cameras, smartphones, music players, and other electronic devices. Their operation is based on high energy density, lack of memory effect, and cost-effectiveness. Overcharge cycles can decrease their capacity, and they discharge when not in use.

Conclusion: Choosing the Right Battery for Your Needs
Choosing between lithium polymer (LiPo) and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries is a critical decision impacting device performance and longevity. LiPo batteries offer a lightweight, flexible design ideal for slim devices but may be prone to swelling. Li-ion batteries provide high energy storage and stable performance, commonly found in laptops and electric vehicles. Safety practices are crucial for both. The best choice depends on specific device needs, considering factors like size, weight, and intended applications.
FAQs
Which is better: lithium-ion or lithium polymer?
Both lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries have their advantages and disadvantages. Li-ion batteries are more common and offer higher energy density, making them suitable for many applications. LiPo batteries, on the other hand, are lighter, more flexible in shape, and can provide higher discharge rates. The choice between the two depends on specific requirements such as energy density, form factor, and discharge characteristics.
Is charging Li-ion better than LiPo?
Charging methods for Li-ion and LiPo batteries are similar, but LiPo batteries typically require more care due to their higher susceptibility to damage from overcharging, over-discharging, or improper handling. Both types of batteries should be charged using appropriate chargers and following manufacturer guidelines to ensure safety and longevity.
Can I replace a lithium-ion battery with a lithium polymer?
In many cases, you can replace a lithium-ion battery with a lithium polymer battery, but factors such as size, voltage, capacity, and safety considerations must be taken into account. It’s essential to ensure compatibility with the device and follow manufacturer recommendations to avoid potential issues.
How long do lithium-polymer batteries last?
The lifespan of lithium-polymer batteries varies depending on factors such as usage patterns, charging practices, and environmental conditions. On average, a well-maintained LiPo battery can last several hundred charge-discharge cycles before experiencing significant degradation.

What are the disadvantages of lithium-polymer batteries?
Disadvantages of lithium-polymer batteries include their higher susceptibility to damage from overcharging, over-discharging, or physical abuse compared to other battery types. They also tend to have lower energy density and slightly higher manufacturing costs.
What lasts longer: lithium-ion or lithium polymer?
The lifespan of both lithium-ion and lithium polymer batteries depends on various factors, including usage patterns and environmental conditions. Generally, both types can have similar lifespans if properly maintained and used within their specified parameters.
Can I charge a lithium polymer battery with a lithium ion charger?
It is not recommended to charge a lithium polymer battery with a charger specifically designed for lithium-ion batteries unless the charger explicitly supports both types of batteries. Using an incompatible charger may lead to overcharging, overheating, or other safety hazards.
Which is better: LiFePO4 vs. LiPo?
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries offer advantages such as better thermal stability, longer cycle life, and improved safety compared to traditional LiPo batteries. However, LiFePO4 batteries typically have lower energy density and higher cost, making them suitable for specific applications where safety and longevity are paramount.