Navigating the world of batteries and automotive technology can often feel like diving into a sea of acronyms and technical specifications. From understanding the difference between MCA, CCA, and HCA, to deciphering standards such as DIN and JIS, there’s a lot to unpack. Moreover, the significance of metrics like Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Reserve Capacity can’t be understated when it comes to ensuring optimal performance for your vehicle.
What Is CCA?
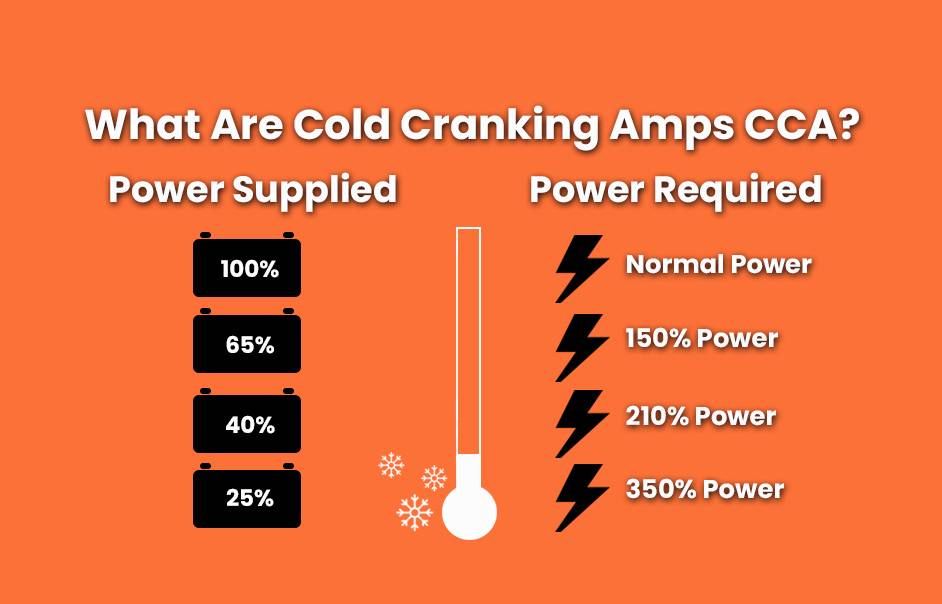
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a crucial specification that determines the battery’s ability to start your vehicle in cold weather conditions. It measures the amount of current a battery can deliver for 30 seconds at 0°F without dropping below 7.2 volts. Essentially, the higher the CCA rating, the easier it is for your car to start in cold temperatures.
When you turn the key in your car on a chilly morning, the CCA rating is what ensures your engine roars to life without any hesitation. A higher CCA rating means a stronger ability to power your vehicle’s starter motor, providing the necessary energy to get your engine running smoothly. Understanding the significance of Cold Cranking Amps can help you choose the right battery for your vehicle, ensuring reliable performance even in the coldest of weather conditions.
What Is CA?
Following the winding roads of discovery, we come to the intriguing realm of CA. Picture a vast landscape stretching before you, with rolling hills and lush greenery as far as the eye can see. CA, short for Certificate Authority, is like a trusted guide in this digital terrain. Just as a seasoned explorer relies on a trusty map, CA provides a secure pathway for data to travel across the internet.
Imagine a bustling marketplace where merchants and customers from all corners of the globe converge to exchange goods and information. In this bustling digital marketplace, CA stands as a vigilant sentinel, ensuring that transactions are safe and secure. Like a watchful guardian, it verifies the identities of websites, encrypts sensitive data, and safeguards against cyber threats.
As the sun sets on another day in the virtual world, CA remains steadfast in its mission to protect and uphold the integrity of online communication. So, next time you browse the web or make an online purchase, remember the unsung hero that is CA, silently working behind the scenes to keep your information safe and secure.
MCA, CCA, and HCA – What’s the Difference?
Diving into the world of MCA, CCA, and HCA, it’s essential to understand the standards that govern them. DIN Standard, originating from Germany, ensures quality and safety in materials. On the other hand, JIS Standard, rooted in Japan, focuses on industrial standards. Now, let’s delve into HCA and PHCA – the key players in the preservation of wood. HCA, or Copper Azole, protects against decay and insects, while PHCA, or Propiconazole Azole, is a fungicide that prevents mold and mildew.
WHAT IS DIN STANDARD?
Curious about the various standards related to corrosion protection coatings? Let’s delve into the world of DIN, a standard that plays a crucial role in the industry. DIN, short for Deutsches Institut für Normung (German Institute for Standardization), sets guidelines for various products and processes to ensure consistency and quality. When it comes to corrosion protection coatings, DIN standards provide specifications for materials, testing methods, and performance requirements. These standards help manufacturers produce coatings that meet specific criteria for durability, adhesion, and resistance to environmental factors. By following DIN standards, companies can ensure that their coatings are reliable and effective in protecting surfaces from corrosion. Understanding and adhering to DIN standards is essential for ensuring the quality and performance of corrosion protection coatings in various industries. Let’s explore more about DIN standards and their significance in the realm of corrosion protection coatings.
WHAT IS JIS STANDARD?
Curious to learn about the JIS standard? Just like the DIN standard, the JIS standard is a set of guidelines developed by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. JIS standards are used in various industries in Japan to ensure products meet specific quality and safety requirements.
JIS standards cover a wide range of products, from industrial equipment to consumer goods. They provide a universal language for manufacturers and consumers, helping to streamline production processes and promote product reliability.
Compliance with JIS standards is crucial for companies looking to enter the Japanese market, as it demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety. By adhering to JIS standards, manufacturers can enhance their reputation and build trust with Japanese consumers.
Understanding the JIS standard is essential for anyone involved in international trade or manufacturing, as it plays a significant role in shaping the Japanese market landscape.
What Are HCA And PHCA?
As we delve into the realm of standards and certifications, let’s now explore the fascinating world of HCA and PHCA. These certifications, known as High Carbon Abrasion and High Precision High Carbon Abrasion, play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and durability of various products. HCA focuses on the carbon content and abrasion resistance of materials, making it ideal for industries where wear and tear are common occurrences. On the other hand, PHCA takes it a step further by emphasizing precision in carbon content, providing an even higher level of durability and performance. Imagine a world where products are built to withstand the test of time, where quality is not just a standard but a guarantee. HCA and PHCA embody this vision, setting the bar high for excellence and reliability in manufacturing. Let’s unravel the significance of these certifications and how they shape the products we use every day.
Impacts of Cold Cranking Amps On Engines
Transitioning from the discussion of cold cranking amps in lithium batteries, let’s explore the significance of CCAs in jump starters. Understanding how many CCAs you need can make a difference in successfully starting your engine. Moving forward, when considering a battery replacement, it’s crucial to take into account factors such as the size, type, and quality of the battery. These considerations can impact your engine’s performance and longevity. By being mindful of these details, you can ensure that your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Let’s delve deeper into the impacts of cold cranking amps on engines.
Do Lithium Batteries Use Cold Cranking Amps?
Continuing our exploration of the impacts of Cold Cranking Amps on engines, let’s delve into the question: do lithium batteries use Cold Cranking Amps? Lithium batteries, known for their lightweight and high energy density, have become increasingly popular in various applications. Unlike traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries do not rely on Cold Cranking Amps for starting power.
Instead, lithium batteries are rated by their cranking amps, which represent the maximum current a battery can deliver for a short period. This distinction is important to note when considering the compatibility of jump starters and battery replacements for vehicles equipped with lithium batteries. Understanding the specific power requirements of lithium batteries can help ensure optimal performance and longevity for your vehicle’s electrical system. So, next time you’re in the market for a new battery, be sure to consider the unique characteristics of lithium batteries and their different power rating systems.

How Many CCAs Do I Need In A Jump Starter?
As we delve into the world of cold cranking amps, one important question that often arises is, “How many CCAs do I need in a jump starter?” Imagine being on a chilly winter morning, your engine struggling to come to life. A reliable jump starter with the right amount of CCAs could be your saving grace in such a situation.
When determining the number of CCAs required in a jump starter, consider the size and type of your vehicle’s engine. Larger engines typically need more CCAs to start up efficiently, while smaller engines may require fewer. It is recommended to have at least 400 to 600 CCAs in a jump starter for most standard vehicles. However, if you drive a larger vehicle or live in an extremely cold climate, you may want to opt for a jump starter with higher CCAs to ensure a quick and successful start every time. Choose wisely and never be left stranded in the cold again!
What Should I Consider When Getting A Battery Replacement?
Imagine you’re on the hunt for a new battery replacement for your vehicle. As you browse through the options, you come across various specifications to consider. One crucial factor to keep in mind is the Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating of the battery. When selecting a battery replacement, it’s essential to consider the CCA rating that matches the requirements of your vehicle’s engine.
To ensure a smooth start, opt for a battery with a CCA rating that meets or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommendations. This will help provide the necessary power to kickstart your engine, especially during cold weather conditions. Additionally, consider the battery’s reserve capacity, warranty, and overall quality to make the best choice for your vehicle. By evaluating these factors when getting a battery replacement, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity for your vehicle’s electrical system.
Where Can I Get Advice On Battery Replacement?
If you are considering replacing your car battery and are unsure where to turn for advice, there are several reliable sources you can consult. One of the best places to seek guidance on battery replacement is your local auto parts store. These stores typically have knowledgeable staff who can help you select the right battery for your vehicle based on its make, model, and specific requirements.
Another great resource for advice on battery replacement is your vehicle’s manufacturer. Many automakers provide information on the recommended battery type and specifications for their vehicles. You can often find this information in your owner’s manual or by contacting the manufacturer directly.
Additionally, online forums and communities dedicated to automotive maintenance and repair can be valuable resources for obtaining advice on battery replacement. These forums often have experienced car enthusiasts and mechanics who are willing to share their knowledge and offer guidance on selecting and installing a new battery for your vehicle.
By seeking advice from these sources, you can make an informed decision when it comes to replacing your car battery and ensure that your vehicle continues to run smoothly.
What is Considered to Be a Good CCA Rating for a Battery?
If you’re in the market for a new battery, you might be wondering what constitutes a good Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating. Considered by many as a crucial factor in a battery’s performance, the CCA rating indicates the amount of current a battery can deliver at 0°F for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts.
Typically, a higher CCA rating is indicative of a battery’s ability to start your vehicle in cold weather conditions. While the exact number can vary depending on your specific vehicle and climate, a good rule of thumb is to look for a battery with a CCA rating that meets or exceeds your manufacturer’s recommendations.
For most standard vehicles, a CCA rating between 600-800 should suffice, providing reliable starting power in various weather conditions. However, if you live in an extremely cold climate, you may want to opt for a battery with a higher CCA rating to ensure optimal performance during those frosty mornings.
Remember, choosing a battery with the right CCA rating can make all the difference in starting your vehicle with ease, no matter the weather conditions. So, keep this in mind when selecting your next battery for a hassle-free driving experience.
What Does a Battery’s Reserve Capacity Measure?
Now that we understand what a good CCA rating signifies for a battery’s performance, let’s delve into another crucial measure: reserve capacity.
Imagine your car stranded on a deserted road, the engine refusing to start. This is where a battery’s reserve capacity comes into play, acting as a beacon of hope in the face of unexpected challenges. Reserve capacity is the amount of time a fully charged battery can continuously supply a minimum voltage needed to keep your vehicle running in case the alternator fails. It is like a safety net, providing you with extra time to reach a safe location or seek help in times of crisis.
Measured in minutes, a higher reserve capacity indicates a battery’s ability to sustain power for a longer duration, offering you peace of mind during long journeys or unforeseen emergencies. It is a testament to the battery’s reliability and readiness to support you when you need it the most. So, when evaluating a battery’s performance, consider not only its CCA rating but also its reserve capacity to ensure a dependable power source for your vehicle.
BU-902a: How to Measure CCA
Imagine standing in a cold, frosty morning, with the hood of a car raised and a multimeter in hand. In the world of battery testing, one of the essential measurements is Cold Cranking Amps (CCA). This value indicates the battery’s ability to deliver a strong burst of power in cold weather conditions, crucial for starting your vehicle on a chilly winter morning.
To measure CCA accurately, you will need a digital multimeter capable of reading high currents. Begin by ensuring the vehicle is turned off and disconnected from any power source. Connect the multimeter to the battery terminals, observing the correct polarity. With the multimeter set to measure current, slowly crank the engine and note the highest current reading displayed. This number represents the CCA of your battery.
Maintaining a healthy CCA value is vital for ensuring your battery can start your vehicle reliably, especially during cold weather. Regularly testing and monitoring your battery’s CCA will help you identify any decline in performance and allow you to take proactive measures to prevent unexpected breakdowns. So, grab your multimeter and get ready to measure the heartbeat of your vehicle’s starting power.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding cold cranking amps is essential for maintaining a healthy engine. By knowing the difference between CA, MCA, CCA, and HCA, you can make informed decisions about your battery replacement needs. A good CCA rating for a battery can ensure reliable starting power in cold weather, while a battery’s reserve capacity measures its ability to run on auxiliary power. Seeking advice on battery replacement from professionals can provide you with the guidance needed to make the best choice for your vehicle.
Remember, knowing how to measure CCA can help you determine the health of your battery and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Taking the time to educate yourself on cold cranking amps can save you time, money, and frustration in the long run. So, the next time you’re in need of a battery replacement, keep these factors in mind to ensure a smooth and efficient start every time.