Explore the game-changing world of Tesla’s batteries – the 21700 and 20700 models. Tesla, known for leading in electric vehicles and renewable energy, brings innovation to energy storage. Learn why these batteries stand out, their benefits, and where they’re used. This blog post is your guide to understanding the brilliance behind Tesla’s latest advancements in powering our future. Get ready for an exciting journey through the electrifying domain of cutting-edge battery technology!
Table of Contents
ToggleDifferences between Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries
When comparing Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries, note their energy storage and usage disparities. Li-ion excels in energy storage, with slower self-discharge compared to Ni-MH. Li-ion uses lithium ions, while Ni-MH combines nickel and metal hydride. Understanding these distinctions aids in choosing the right battery type.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Energy Storage: Li-ion batteries store more energy compared to Ni-MH batteries. For example, a typical Li-ion battery used in smartphones can hold about 150% more energy than a Ni-MH battery of the same size.
- Longevity: Li-ion batteries have a longer lifespan than Ni-MH batteries. Studies show that Li-ion batteries can endure more charge and discharge cycles before losing their capacity. On average, Li-ion batteries can last about 2-3 times longer than Ni-MH batteries.
- Environmental Impact: Li-ion batteries are generally considered to have a lower environmental impact compared to Ni-MH batteries. This is because Li-ion batteries contain fewer toxic materials, making them easier to recycle and dispose of responsibly.
In conclusion, Li-ion batteries outperform Ni-MH batteries in terms of energy storage, longevity, and environmental impact. Understanding these differences can help individuals and businesses choose the most suitable battery type for their needs.
Advantages of Li-ion batteries
- High Energy Density: Li-ion batteries can store a large amount of energy in a compact size.
- Fast Charging: Li-ion batteries can be charged at a faster rate compared to other battery technologies.
- Low Maintenance: Li-ion batteries require minimal maintenance tasks, reducing the need for regular upkeep.
- Environmental Friendliness: Li-ion batteries are more environmentally friendly as they do not contain toxic materials like lead or cadmium.
- Low Self-Discharge: Li-ion batteries have a low self-discharge rate, allowing them to retain their charge for longer periods.
- Lightweight and Compact: Li-ion batteries are lightweight and have a compact design, making them suitable for portable devices.
- Long Lifespan: Li-ion batteries have a longer lifespan, offering more charge and discharge cycles.
- Good Performance at High Temperatures: Li-ion batteries perform well even in high-temperature conditions.
Advantages of Ni-MH batteries
Ni-MH batteries offer advantages such as higher power and energy density, a much longer life cycle compared to lead-acid batteries, safe operation, and minimal memory effect. These advantages make Ni-MH batteries a preferred choice for various applications, from portable electronics to hybrid vehicles.

- Higher Power and Energy Density: Ni-MH batteries offer higher power and energy density compared to lead-acid batteries, resulting in more efficient energy storage.
- Longer Life Cycle: Ni-MH batteries have a much longer life cycle, allowing for more charge-discharge cycles and extended usage.
- Safe Operation: Ni-MH batteries are considered safe, with no risk of leakage or explosion.
- Minimal Memory Effect: Ni-MH batteries exhibit a reduced memory effect, allowing for recharging at any time without the need for full discharge.
Disadvantages of Li-ion batteries
- Fragility: Li-ion batteries can be fragile and require a protection circuit to ensure safe operation.
- Protection Circuit: The protection circuit limits the voltage during charge and discharge, maintaining safe voltage levels.
- Safety Measures: The protection circuit prevents overcharging and voltage drop, ensuring the battery’s safety and longevity.
Disadvantages of Ni-MH batteries
- Higher Cost: Ni-MH batteries can be more expensive compared to other battery types.
- Strong Self-Discharge Rate: Ni-MH batteries have a higher self-discharge rate, meaning they lose their charge over time even when not in use.
- Heat Generation: Ni-MH batteries generate heat at extreme temperatures, which can affect their performance and lifespan.
Performance comparison between Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries
- Energy Density: Li-ion batteries offer higher energy density, providing more power in a smaller size.
- Weight: Li-ion batteries are lighter compared to Ni-MH batteries, making them suitable for portable devices.
- Self-Discharge Rate: Li-ion batteries have a lower self-discharge rate, retaining their charge for longer periods.
- Cost: Ni-MH batteries are generally more cost-effective compared to Li-ion batteries.
- Capacity: Ni-MH batteries typically have higher capacity, providing longer usage times.
Factors to consider when choosing between Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries
When choosing between Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries, factors to consider include cycle life, battery weight, memory effect, environmental issues, and cost. Li-ion batteries generally offer a longer cycle life, lighter weight, no memory effect, recyclability, and higher cost. Ni-MH batteries have a shorter cycle life, heavier weight, potential memory effect, recyclability, and lower cost.
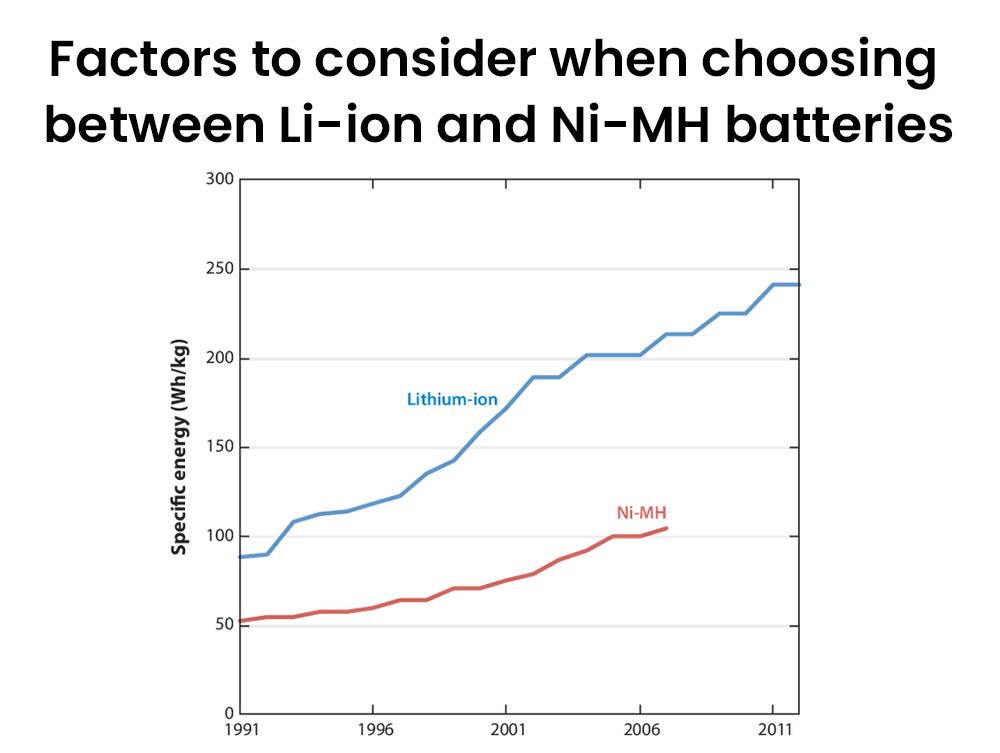
- Cycle Life: Li-ion batteries generally have a longer cycle life compared to Ni-MH batteries.
- Battery Weight: Li-ion batteries are lighter in weight, making them suitable for portable devices.
- Memory Effect: Li-ion batteries do not suffer from memory effect, while Ni-MH batteries may experience this phenomenon.
- Environmental Impact: Both Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries are recyclable, contributing to sustainable practices.
- Cost: Li-ion batteries tend to be more expensive than Ni-MH batteries.
Best uses for each type of battery
Considering the unique characteristics of Li-ion and Ni-MH batteries, let’s explore their best uses.
Li-ion Batteries
- Portable Electronics: Li-ion batteries power smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other portable electronic devices due to their high energy density and lightweight.
- Electric Vehicles: Li-ion batteries are used in electric vehicles for their ability to provide reliable and long-lasting power, enabling emission-free transportation.
- Power Tools: Li-ion batteries are preferred for power tools due to their high power output and longer runtimes, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Li-ion batteries play a crucial role in storing renewable energy generated from sources like solar and wind, ensuring a stable power supply.
Ni-MH Batteries
- Digital Cameras: Ni-MH batteries are commonly used in digital cameras due to their ability to handle high-drain requirements.
- Communication Equipment: Ni-MH batteries power communication devices that require reliable and long-lasting power sources.
- Personal Cosmetics Equipment: Ni-MH batteries find use in personal cosmetics equipment, providing portable and efficient power for beauty devices.
FAQs
Do NiMH or Lithium Ion Batteries Need a Special Charger?
- Battery-Specific Chargers: NiMH batteries require chargers designed specifically for NiMH batteries, while lithium-ion batteries need chargers designed for lithium-ion batteries.
- Proper Charging: Using the correct charger ensures the batteries are charged according to their specific requirements, preventing overcharging or undercharging.
- Optimal Performance and Safety: Using the appropriate charger for each battery type ensures optimal charging, longer battery life, and reduces the risk of safety hazards.
Should You Fully Discharge NiMH Batteries?
- Memory Effect: Older generation NiMH batteries were believed to develop a memory effect, requiring full discharge before recharging to maintain capacity.
- New Generation Batteries: The new generation of NiMH batteries does not develop a memory effect and can be recharged at any time during the usage cycle.
- Convenience and Flexibility: The absence of a memory effect allows users to recharge NiMH batteries as needed, providing convenience and flexibility.
Can I replace NiMH with Lithium Ion?
- Non-Interchangeability: In most cases, NiMH and lithium-ion batteries are not interchangeable due to differences in size, shape, and voltage.
- Device-Specific Compatibility: The compatibility of battery types depends on the specific device and its requirements.
- User’s Manual: The user’s manual of the device should provide information on the compatibility and recommended battery types.
What is a Lithium Ion Battery?
- Rechargeable Design: Lithium-ion batteries can be charged and discharged multiple times, making them suitable for various applications.
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, providing a longer-lasting power source for devices.
- Wide Range of Applications: Lithium-ion batteries are used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems, among other applications.
Which is Better, NiMH or Lithium Ion Battery?
- NiMH Batteries: NiMH batteries are generally cheaper and have a longer overall life expectancy.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, lighter weight, and better charge retention.
- Specific Applications: The choice between NiMH and lithium-ion batteries depends on specific requirements, such as cost, longevity, energy density, and weight.
Can NI-MH batteries be charged using a lithium battery charger?
- Different Chemistries: NI-MH and lithium batteries have different chemical compositions and characteristics.
- Voltage Requirements: NI-MH batteries require a specific voltage range for optimal charging, different from that of lithium batteries.
- Improper Charging: Using a lithium battery charger for NI-MH batteries can result in improper charging, reducing battery life and potentially causing safety hazards.
Which type of battery, NI-MH or lithium-ion, is safer to use?
- Ni-MH Battery Safety: Ni-MH batteries are generally considered safer than lithium-ion batteries due to their lower risk of thermal runaway and reduced sensitivity to overcharging.
- Lithium-Ion Battery Safety: While lithium-ion batteries have a higher risk of thermal runaway and overcharging, proper safety measures such as temperature monitoring and voltage regulation can mitigate these risks.
- Precautions: Regardless of the battery type, it is important to follow safety guidelines, such as using appropriate chargers, avoiding overcharging, and storing batteries in a cool and dry place.
Both Ni-MH and lithium-ion batteries have safety considerations. Ni-MH batteries generally have a lower risk of thermal runaway, while lithium-ion batteries require proper safety measures. Following safety guidelines and precautions ensures the safe use of both battery types.
Will a Flashlight Shine Brighter with a Higher Voltage Lithium Battery?
-
Voltage and Brightness: A higher voltage battery, like lithium, can provide more power to the flashlight, potentially resulting in a brighter light output.
-
Design and Efficiency: The design and efficiency of the flashlight also play a significant role in determining its brightness. A well-designed flashlight with efficient components can maximize the use of the battery’s power.
-
Consider Overall Performance: When selecting a battery for your flashlight, consider its compatibility and overall performance with the flashlight to achieve the desired brightness and optimal performance.
Does Higher Voltage Lithium Make a Torch Brighter?
-
Voltage and Brightness: A higher voltage battery, like lithium, can provide more power to the torch, potentially resulting in a brighter light output.
-
Design and Efficiency: The design and efficiency of the torch, including the quality of the LED and reflector, also influence brightness. A well-designed torch can maximize the use of the battery’s power.
-
Compatibility: Ensure that the torch is compatible with the higher voltage lithium battery to achieve optimal performance. Check the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery compatibility.
Is Battery Leakage Possible for Both NiMH and Lithium?
-
NiMH Battery Leakage: NiMH batteries are more prone to leakage when overcharged or exposed to extreme temperatures. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging and avoid subjecting them to extreme conditions.
-
Lithium Battery Sealed Construction: Lithium batteries have a lower risk of leakage due to their sealed construction. However, it’s still essential to handle them with care and avoid physical damage that could compromise their integrity.
-
Proper Handling and Storage: Regardless of the battery type, proper handling and storage are crucial to minimize the risk of leakage. Avoid overcharging, extreme temperatures, and physical damage to ensure the safe use of batteries.
Which Provides Better Runtime in an LED Torch: NiMH or Lithium?
-
Lithium Battery Runtime: Lithium batteries have a higher energy density, allowing them to deliver more power and provide better runtime in an LED torch. This makes them suitable for applications that require longer operating times.
-
NiMH Battery Runtime: NiMH batteries have a lower energy density compared to lithium batteries, resulting in relatively shorter runtime in an LED torch. However, advancements in NiMH technology have improved their performance over time.
-
Consider Power Consumption and Efficiency: In addition to the battery type, factors such as the torch’s power consumption and efficiency also impact runtime. A well-designed and energy-efficient LED torch can maximize the use of the battery’s power, regardless of the battery type.
Why Might Lithium Batteries Make a Flashlight Brighter?
Lithium batteries can make a flashlight brighter by delivering higher energy density compared to other battery types. With their ability to store more energy per unit volume, lithium batteries provide increased power to the LEDs, resulting in a brighter and more intense light output. However, it is crucial to use well-designed LED flashlights with current-limiting circuitry to ensure safe and optimal performance. By utilizing lithium batteries, users can experience enhanced brightness and illumination for various applications.
How Does Higher Voltage Lithium Affect Torch Brightness?
Higher voltage lithium batteries can impact torch brightness by providing a power boost to the flashlight’s LEDs. With their higher voltage compared to other battery types, lithium batteries can deliver more power and increase the brightness of the torch. However, it is essential to consider other factors, including the design and efficiency of the flashlight’s circuitry, which also play a role in determining the overall brightness.
Is Battery Leakage Possible for NiMH and Lithium?
Which Provides Better LED Torch Runtime: NiMH or Lithium?
When comparing the runtime of LED torches, the choice between NiMH and lithium batteries depends on various factors. While lithium batteries generally have a higher capacity and can provide longer runtime, it is crucial to consider other factors such as the voltage output and the design of the torch. NiMH batteries, although having a lower capacity, can still provide sufficient runtime depending on the specific flashlight and usage requirements. It is recommended to consider the specific needs and characteristics of the torch when selecting the battery type for optimal runtime.













