Are you tired of worrying about your phone’s battery life and constantly searching for a charging outlet? The 30-80 Charging Rule might be the solution you need. In this blog post, we’ll explore what this rule entails and how it can help extend your device’s battery lifespan, making charging more efficient. Say goodbye to midday power struggles and hello to a smarter charging routine! Let’s dive in!
Understanding the 30 80 Charging Rule
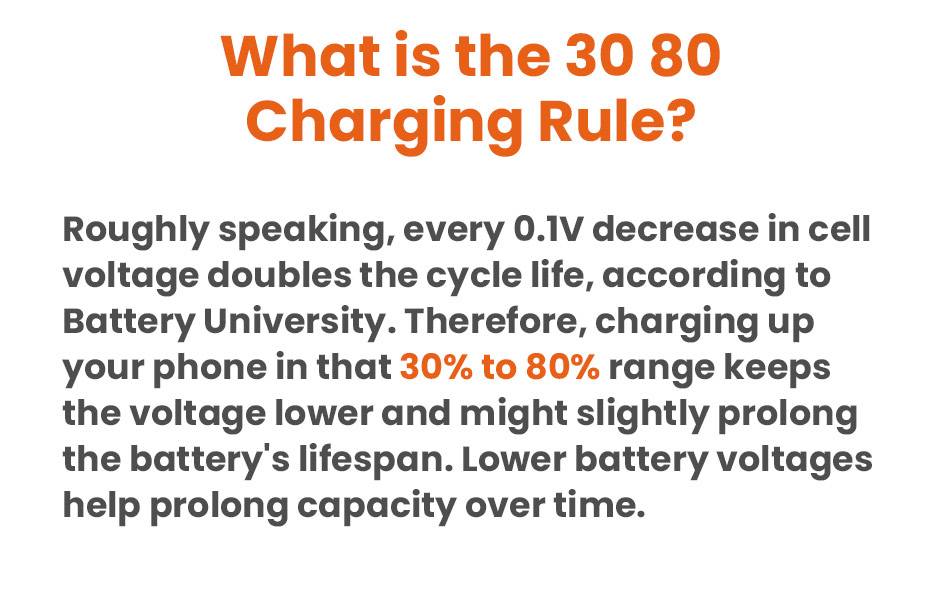
The 30 80 Charging Rule is a simple guideline aimed at optimizing your device’s battery lifespan. By avoiding letting your battery drop below 30% or exceed 80% charge, you can reduce strain on its cells and prolong its overall capacity.

- Why it Matters: Charging your phone from low levels (e.g., 20%) strains battery cells, reducing their capacity over time. Similarly, charging above 80% can stress the battery, diminishing its longevity.
- Maintaining Safe Range: Following the 30 80 rule ensures your battery operates within a safe range, preventing unnecessary wear and tear and extending its lifespan.
- Monitoring Made Easy: Most smartphones now offer Battery Health features, displaying real-time percentages and sending notifications for optimal charging, making it easier to adhere to the rule and maximize battery longevity.
How the Rule Works
The 30 80 Charging Rule is a guideline for managing credit card balances effectively to maintain good credit scores. But how does it work?
- Understanding Credit Utilization Ratio: It’s the amount of available credit you’re currently using. Keeping this ratio low is crucial for a healthy credit score.
- 30% Limit for Individual Cards: The rule advises keeping balances below 30% of each card’s credit limit. For example, if your limit is $10,000, aim to keep your balance under $3,000.
- 80% Limit Across All Cards: Additionally, ensure the combined balances across all cards don’t exceed 80% of the total credit limits. This helps demonstrate responsible credit usage and can positively impact your financial health.
Pros and Cons of the 30 80 Charging Rule
The 30 80 Charging Rule is a strategy for managing time and energy effectively. Let’s explore its pros and cons.
- Pros:
- Promotes Focus and Productivity: By allocating 30% of time to high-priority tasks and 80% to important but less urgent ones, it helps accomplish more in a structured manner.
- Encourages Balance: Ensures time for both immediate deadlines and long-term goals, fostering a healthier work-life balance and preventing burnout.
- Cons:
- May Not Suit Everyone: Some individuals may prefer more flexibility in their routines, while certain jobs or industries might require different approaches.
- Risk of Rigidity: Strict adherence to percentages could lead to inflexibility in scheduling, necessitating adaptability to changing circumstances or opportunities.
While the 30 80 Charging Rule offers benefits like increased productivity and balance, it’s essential to consider personal preferences and circumstances to find the most suitable approach.
Common Misconceptions about the Rule
Let’s debunk some common misconceptions surrounding the 30 80 Charging Rule, a popular time management technique.
- Misconception: Promotes Procrastination:
- Some believe that the rule encourages laziness by allowing breaks during work hours. However, it actually emphasizes focused productivity within specific timeframes while acknowledging the importance of rest.
- Misconception: Leads to Burnout:
- Critics argue that adhering strictly to the rule interrupts workflow and efficiency. Yet, with proper planning and discipline, individuals can overcome challenges and maintain a productive rhythm.
- Misconception: Neglects Personal Life:
- There’s a fear that following the rule means sacrificing personal interests for career goals. However, effective time management allows for both professional success and pursuing passions outside of work.
- Misconception: Restricts Creativity:
- Some feel confined by strict percentages, fearing it stifles spontaneity. However, integrating flexibility while adhering to core principles can strike a balance between structure and creativity.
Addressing these misconceptions helps us grasp the true essence and benefits of the 30 80 Charging Rule in optimizing time management.
Examples of Applying the Rule in Real Life Scenarios
Let’s explore practical examples of how the 30 80 Charging Rule can be applied in real-life situations to enhance productivity and time management.

- Freelance Graphic Designer (Sarah):
- Sarah dedicates 30% of her workday to high-priority tasks and client meetings, while the remaining 80% is focused on completing design projects. This approach ensures she meets deadlines efficiently and maintains quality in her work.
- E-commerce Store Owner (John):
- John allocates 30% of his time to marketing strategies and promotions for his handmade jewelry business. The remaining 80% is dedicated to crafting unique pieces and fulfilling customer orders promptly, maximizing both sales and product quality.
- IT Project Manager (Emma):
- Emma spends around 30% of her schedule on planning, coordinating with stakeholders, and managing resources efficiently. The remaining 80% is devoted to overseeing development stages and ensuring timely delivery of software applications.
These examples demonstrate how individuals across different professions can effectively implement the principles of the 30 80 Charging Rule to streamline their workflow and achieve optimal results in their respective fields.
Alternatives to the 30 80 Charging Rule
While the 30 80 charging rule is popular for managing credit card utilization, it has limitations. Here are some alternative strategies to effectively manage your credit and improve your financial health.
- Pay in Full:
- Paying off your credit card balance in full each month is a highly effective strategy. This avoids carrying debt and minimizes the risk of overspending.
- Utilization Tracking:
- Regularly monitor your overall credit utilization ratio, aiming to keep it below 30% at all times. This approach ensures responsible credit usage regardless of billing cycles.
- Multiple Payments:
- Consider making multiple payments throughout the billing cycle if maintaining low utilization is challenging. This helps lower your balance more frequently, reducing overall utilization.
- Increase Credit Limit:
- Contact your credit card issuer to request a higher credit limit or explore accounts with higher limits. Increasing available credit while spending responsibly can naturally lower your utilization ratio.
- Balance Transfers:
- Explore balance transfers to consolidate high-interest balances onto cards with lower rates. This can streamline debt management and provide breathing room for repayment.
Conclusion: While the 30 80 charging rule offers a simple guideline, it’s essential to explore alternative strategies based on your unique financial situation and goals. Being mindful of your overall credit utilization ratio and implementing effective payment practices are key to maintaining a healthy financial profile.