Battery acid is a crucial component of lead-acid batteries, commonly found in automotive and marine applications. While essential for battery function, it poses serious risks to health and the environment. Let’s explore the dangers of battery acid and safety precautions to mitigate these risks, along with the emergence of safer lithium battery alternatives.
What is the Composition of Battery Acid?
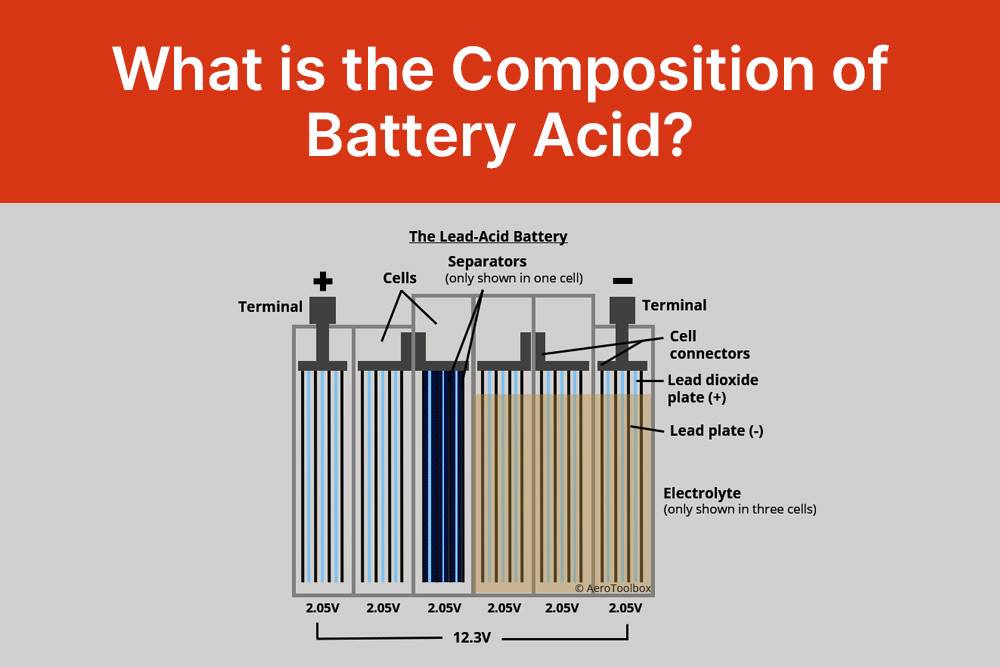
Battery acid, the vital component of lead-acid batteries, predominantly consists of a diluted sulfuric acid solution. Typically, it contains 30-50% sulfuric acid mixed with distilled water. This specific composition is essential for the functionality of lead-acid batteries, as sulfuric acid plays a pivotal role in facilitating the chemical reactions necessary for electricity production. Through a series of reactions, sulfuric acid enables the conversion of lead and lead dioxide into lead sulfate, along with the generation of electrical energy. This chemical process is fundamental to the functioning of various automotive, marine, and other applications reliant on lead-acid batteries. Understanding the composition of battery acid is crucial for ensuring proper handling and maintenance of lead-acid battery systems, while also highlighting the significance of safer alternatives like lithium batteries in modern energy storage solutions.
What are the Hazards of Battery Acid
Exposure to battery acid poses significant health and environmental hazards. Inhalation or contact can result in breathing difficulties, skin burns, and internal damage if ingested. Moreover, improper disposal of lead-acid batteries presents environmental risks, adversely affecting plants, animals, and ecosystems. These hazards underscore the importance of handling battery acid with care and ensuring proper disposal methods to safeguard both human health and the environment.
Safety Precautions for Battery Acid
When handling lead-acid batteries, safety precautions are paramount. It’s crucial to wear protective clothing and work in well-ventilated areas to minimize exposure to battery acid fumes. Additionally, using batteries only for their intended purposes helps mitigate risks associated with mishandling. Furthermore, keeping batteries away from children is essential to prevent accidents. Proper disposal of lead-acid batteries is also critical, ensuring that they are recycled or disposed of in accordance with regulations to prevent environmental harm. These safety measures help reduce the risk of accidents and exposure to hazardous materials, promoting a safer environment for both individuals and ecosystems.

Transition to Lithium Batteries
Modern lithium battery technology offers a safer alternative to lead-acid batteries. Lithium batteries are maintenance-free, produce no harmful vapors, and can be installed in living spaces. Transitioning to lithium batteries eliminates the risks associated with battery acid exposure.
In summary, understanding the dangers of battery acid and implementing safety measures is essential for minimizing health and environmental hazards. Transitioning to safer lithium battery options ensures reliable power without the risks associated with lead-acid batteries.
FAQs
What are the main hazards associated with battery acid exposure?
Exposure to battery acid can result in breathing difficulties, skin burns, and internal damage if ingested. Improper disposal also poses environmental risks, harming plants, animals, and ecosystems.
How can I protect myself from battery acid exposure?
Wear protective clothing, work in well-ventilated areas, and handle batteries only for their intended purposes. Keep batteries away from children, and ensure proper disposal to minimize risks.
What are the safety precautions to take when working with lead-acid batteries?
Wear protective clothing, such as goggles and gloves, and work in well-ventilated areas. Only use batteries for their intended purposes and keep them out of reach of children. Properly dispose of used batteries to prevent environmental harm.

Why should I consider transitioning to lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries offer a safer alternative to lead-acid batteries. They are maintenance-free, produce no harmful vapors, and can be installed in living spaces. Transitioning eliminates the risks associated with battery acid exposure.
What steps should I take for proper disposal of old lead-acid batteries?
Take old batteries to auto parts retailers or battery stores for recycling. Many places offer free recycling services. Never throw them in regular trash to prevent environmental contamination.
Are there any environmental benefits to transitioning to lithium batteries?
Yes, transitioning to lithium batteries reduces environmental harm by eliminating the disposal of lead-acid batteries, which contain harmful chemicals. Additionally, lithium batteries produce no harmful emissions during use.

