- Forklift Lithium Battery
- Golf Cart Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
51.2V 100Ah Rackmount LiFePO4 Battery
8000 times (80% DOD 0.5C)
Optional SNMP for TELECOM - Car Starter Battery
- 12V LiFePO4 Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | Self-heating
LiFePO4 | Group 31
UL 1642 | IEC 62619 - 24V LiFePO4 Battery
- 36V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V LiFePO4 Battery
60V 100Ah Lithium Battery (AGV, AMR, LGV)
Peak Discharge Current 400A
500 x 298 x 349 mm - 72V~96V LiFePO4 Battery
72V 100Ah Lithium Golf Cart Battery
Peak Discharge Current 315A (10S)
740 × 320 × 246 mm - Wall-mounted Lithium Battery
51.2V 100Ah 5kWh
Wall-mounted Battery532 x 425 x 170 mm / LiFePO4
>8000 Cycles (80% DOD 0.5C)
RS485 / CAN-bus
for Solar Home ESS - Home-ESS All-in-One
51.2V 32kWh
All-in-On HESS SystemPowerAll
51.2V / LiFePO4
>8000 Cycles (80% DOD 0.5C)
RS485 / CAN-bus / WiFi
All-in-One for Home ESS
Is It Safe to Charge a LiFePO4 Battery with a Standard Charger?

Charging a Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) battery with a standard charger designed for lead-acid or other battery types is not safe. These batteries require specific charging profiles, and using an inappropriate charger can lead to overcharging, potential damage, and reduced lifespan. Always use chargers specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries.
Why Is It Important to Use the Correct Charger for LiFePO4 Batteries?
Using the correct charger is crucial because LiFePO4 batteries have unique voltage and current requirements that differ from other battery types. A standard charger may not provide the necessary constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile required by these batteries, leading to inefficiencies and safety hazards.Chart: Comparison of Charging Requirements
| Battery Type | Charging Profile | Voltage Range |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Constant Current/Voltage | 12.6V – 14.6V |
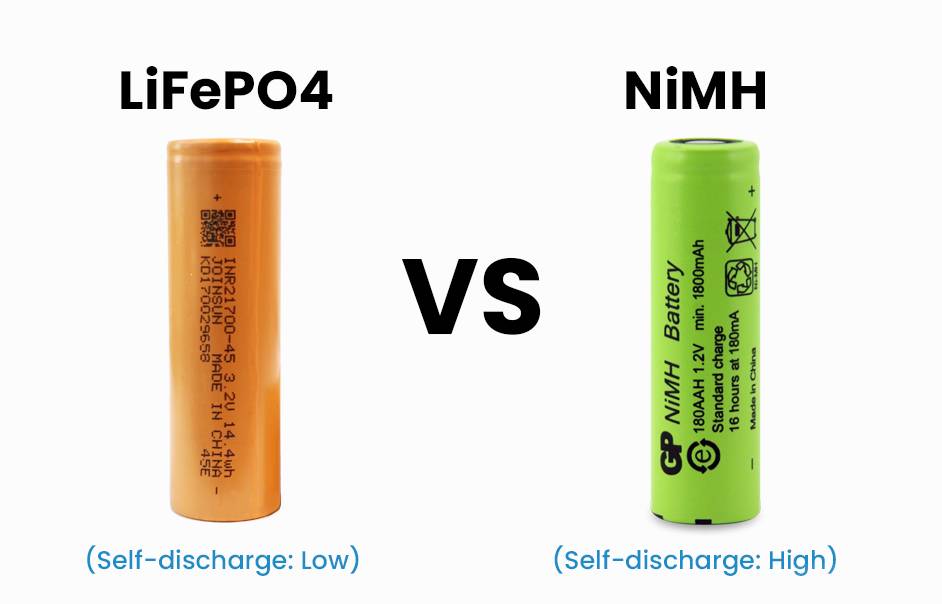
| NiMH | Constant Current | 1.2V per cell |
| LiFePO4 | CC/CV | 14.0V – 14.6V |
What Are the Risks of Charging a LiFePO4 Battery with a Standard Charger?
Charging a LiFePO4 battery with a standard charger can result in several risks:
- Overcharging: Standard chargers may not detect when the battery is fully charged, leading to overcharging, which can cause overheating and damage.
- Reduced Lifespan: Continuous overcharging can degrade battery chemistry, significantly shortening its lifespan.
- Safety Hazards: Overheating can lead to thermal runaway, posing fire risks or even explosions in extreme cases.
How Do Charging Requirements Differ Between LiFePO4 and Other Battery Types?
LiFePO4 batteries require a specific charging method that includes two stages: constant current (CC) followed by constant voltage (CV). In contrast, lead-acid batteries typically use a simple constant current/constant voltage method without the need for specific voltage settings during different charging phases.Chart: Charging Methods Overview
| Battery Type | Charging Method | Stages |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | CC/CV | Single Stage |
| NiMH | CC | Single Stage |
| LiFePO4 | CC followed by CV | Two Stages |
What Is the Recommended Charging Method for LiFePO4 Batteries?
The recommended method for charging LiFePO4 batteries involves:
- Constant Current Phase: Charge at a rate typically between 0.2C and 1C until reaching approximately 14.6 volts per cell.
- Constant Voltage Phase: Maintain voltage at around 14.6 volts while allowing current to taper off until it reaches the cutoff level.
This method ensures efficient charging while protecting battery health.
How Can You Ensure Safe Charging Practices for LiFePO4 Batteries?
To ensure safe charging practices:
- Use Dedicated Chargers: Always utilize chargers specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries.
- Monitor Temperature: Keep an eye on battery temperature during charging; avoid charging in extreme temperatures.
- Regular Inspections: Inspect batteries regularly for signs of damage or swelling before charging.
What Are the Alternatives for Charging LiFePO4 Batteries Safely?
For those without access to dedicated chargers, alternatives include:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): These systems often come with built-in chargers tailored for LiFePO4 batteries.
- Smart Chargers: Some smart chargers can adapt their output based on battery type, but ensure they are compatible with LiFePO4 specifications.
How Can OEM Buyers Source Proper Chargers for LiFePO4 Batteries?
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers:
When sourcing chargers as an OEM buyer, consider partnering with Redway Power, which has over 13 years of experience in lithium battery manufacturing. Key steps include:
- Identify Specifications: Determine the specific voltage and current requirements of your batteries.
- Contact Manufacturers: Reach out to manufacturers like Redway Power who specialize in lithium technologies.
- Request Samples: Before committing, request samples of chargers to test compatibility and performance.
By following these steps, OEM buyers can ensure they source reliable and safe charging solutions.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Charging lithium iron phosphate batteries requires careful attention to detail,” states an expert from Redway Power. “Using standard chargers can lead to serious safety issues and significantly reduce battery life. It’s essential that users invest in proper charging equipment tailored specifically for their battery type.”In conclusion, charging a LiFePO4 battery with a standard charger is unsafe due to distinct charging requirements that must be met to ensure optimal performance and safety. Always use appropriate chargers designed specifically for these batteries to maximize their lifespan and efficiency.
FAQ Section
- Can I use any charger for my LiFePO4 battery?
No, you should use a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries to avoid risks of overcharging and damage. - What happens if I use a lead-acid charger on my LiFePO4 battery?
Using a lead-acid charger can lead to overcharging, reducing your battery’s lifespan and potentially causing safety hazards. - How do I know if my charger is suitable for my battery?
Check the charger’s specifications against your battery’s requirements; it should match the voltage and follow the CC/CV charging profile. - Is it safe to charge my battery at high temperatures?
No, avoid charging at high temperatures as it can lead to overheating and increased risk of thermal runaway. - What should I do if my battery shows signs of swelling?
Stop using the battery immediately, do not charge it further, and consult professionals for safe disposal or inspection.