Blog
What You Need to Know About Battery Discharge
Battery discharge is the process where a battery releases the stored chemical energy as electrical energy to power devices. This involves internal chemical reactions that move electrons through an external circuit, creating current and enabling devices to function. Understanding battery discharge is crucial for optimizing battery life, performance, and safe usage.
What Is Battery Discharge and How Does It Work?
Battery discharge occurs when a battery powers an external load, causing electrons to flow from the negative terminal (anode) to the positive terminal (cathode) through the device. Internally, positive ions move within the electrolyte to balance charge transfer. This electrochemical reaction converts stored chemical energy into electrical current, which continues until the battery’s active materials deplete or voltage drops below operational thresholds.
How Does Voltage Change During Battery Discharge?
As a battery discharges, its terminal voltage gradually decreases from the nominal voltage toward the cutoff voltage. The voltage drop corresponds to the consumption of chemical reactants and internal resistance increase. A stable voltage during discharge means consistent power output, but voltage eventually declines significantly, signaling the battery needs recharging to avoid damage or performance loss.
What Is Depth of Discharge (DoD) and Why Is It Important?
Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to the percentage of the battery’s total capacity that has been used during discharge. For example, a 30% DoD means 30% of the battery’s capacity has been used, leaving 70% remaining. Managing DoD is vital because deeper discharges can accelerate battery wear, reduce cycle life, and degrade performance, while shallow discharges typically extend battery longevity significantly.
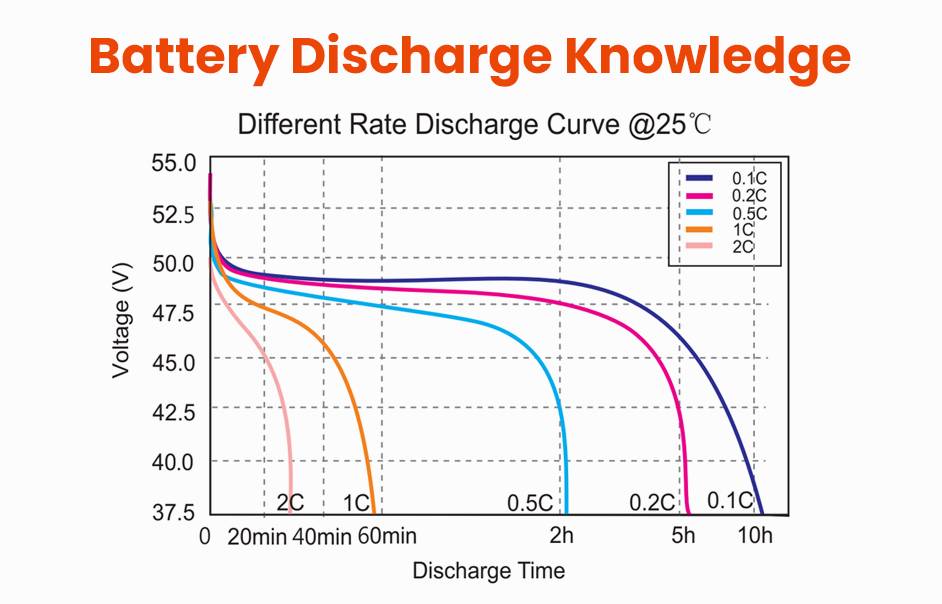
How Does Discharge Rate Affect Battery Capacity and Lifespan?
Discharge rate, often expressed in C-rate (how quickly a battery is discharged relative to its capacity), impacts the effective usable capacity and battery health. Higher discharge rates result in greater internal heat and chemical stress, reducing available capacity due to inefficiencies and accelerating aging. Slower discharge rates conserve capacity and promote longer battery service life.
What Happens When a Battery Is Over-Discharged?
Over-discharging a battery beyond its recommended cutoff voltage causes irreversible damage such as electrolyte breakdown, electrode degradation, and increased internal resistance. This leads to permanent capacity loss, reduced cycle life, and sometimes unsafe conditions like swelling or leakage. Many modern batteries include protection circuits to prevent over-discharge.
How Is Battery State of Charge (SoC) Related to Discharge?
State of Charge (SoC) quantifies how much charge remains in a battery relative to its full capacity, essentially the converse of DoD. SoC monitoring helps users and devices understand how much usable energy is left and when recharging is necessary, preventing deep discharge that damages the battery and ensuring reliable power availability.
How Do Temperature and Environmental Factors Influence Battery Discharge?
Temperature significantly affects battery discharge behavior; low temperatures slow chemical reactions, reducing capacity and voltage output, while high temperatures increase discharge rates and stress internal components, speeding up degradation. Proper temperature management is critical to maintaining battery efficiency and safety during discharge.
How Does Redway Power Improve Battery Discharge Performance and Safety?
Redway Power, with 13 years of experience and ISO certified production, incorporates advanced battery management systems (BMS) and precision manufacturing to optimize discharge characteristics. Their lithium battery packs feature protections against over-discharge, thermal runaway, and cell imbalance, ensuring stable voltage, prolonged cycle life, and safe operation across demanding applications including electric vehicles and energy storage.
Battery Discharge Voltage Profile Chart
| State of Charge (%) | Typical Voltage Range (Li-ion) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | ~4.2 V per cell | Fully charged |
| 80 | ~3.85 V per cell | Normal operating range |
| 50 | ~3.7 V per cell | Mid discharge |
| 20 | ~3.5 V per cell | Low charge warning level |
| 0 | ~3.0 V per cell | Cutoff voltage, recharge needed |
What Are Best Practices for Battery Discharge Management?
- Avoid fully discharging the battery to prevent damage and ensure longer life.
- Use battery management systems to monitor voltage, current, and temperature in real time.
- Maintain appropriate charge/discharge cycles to balance performance and lifespan.
- Store batteries in moderate temperature environments.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines on cutoff voltages and DoD limits.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Effective battery discharge control is the cornerstone of modern battery technology. At Redway Power, we integrate sophisticated battery management systems with precision-engineered lithium-ion chemistry to extend cycle life and maintain optimal performance. Our approach balances discharge efficiency with safety, enabling reliable power delivery even under high-load or extreme environmental conditions critical for today’s electric transport and energy storage needs.” – Senior Engineer, Redway Power
Conclusion
Battery discharge is a complex electrochemical process essential to powering devices but requires careful management to optimize performance and durability. Understanding the relationship between discharge depth, voltage changes, discharge rate, and environmental factors helps users safeguard battery health. Advanced battery producers like Redway Power enable superior discharge management via robust design and cutting-edge controls, promoting longevity and safety across technologies.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between Depth of Discharge and State of Charge?
A: Depth of Discharge (DoD) is the percentage of battery capacity used, while State of Charge (SoC) is the remaining capacity, essentially complementary metrics.
Q: Can over-discharging permanently damage batteries?
A: Yes, over-discharge can cause irreversible chemical damage and reduce battery life or safety.
Q: How does discharge rate affect battery life?
A: Higher discharge rates increase internal stress and heat, reducing capacity and accelerating aging.
Q: What voltage indicates a battery needs recharging?
A: Typically when voltage approaches the cutoff voltage (around 3.0V per cell for Li-ion), recharge is necessary.
Q: How does Redway Power’s battery technology improve discharge safety?
A: Redway Power employs advanced battery management systems for monitoring and protection, ensuring safe discharge profiles and extended battery longevity.