Blog
How Many Watts Is An Amp?

An amp (ampere) itself is a unit of electrical current, not power. To determine how many watts correspond to an amp, you must multiply the current (amps) by the voltage (volts) in the circuit. The formula is Watts = Amps × Volts, meaning the wattage depends on both the current and voltage supplied. This relationship is essential for calculating electrical power in both AC and DC systems.
What Is an Amp and How Is It Different from a Watt?
An ampere (amp) measures the flow rate of electric charge—how many electrons pass a point per second—reflecting electrical current. A watt measures electrical power, which quantifies the rate of energy transfer or consumption. Watts depend on the product of current (amps) and voltage (volts), combining how much current flows and the pressure (voltage) pushing it through a circuit.
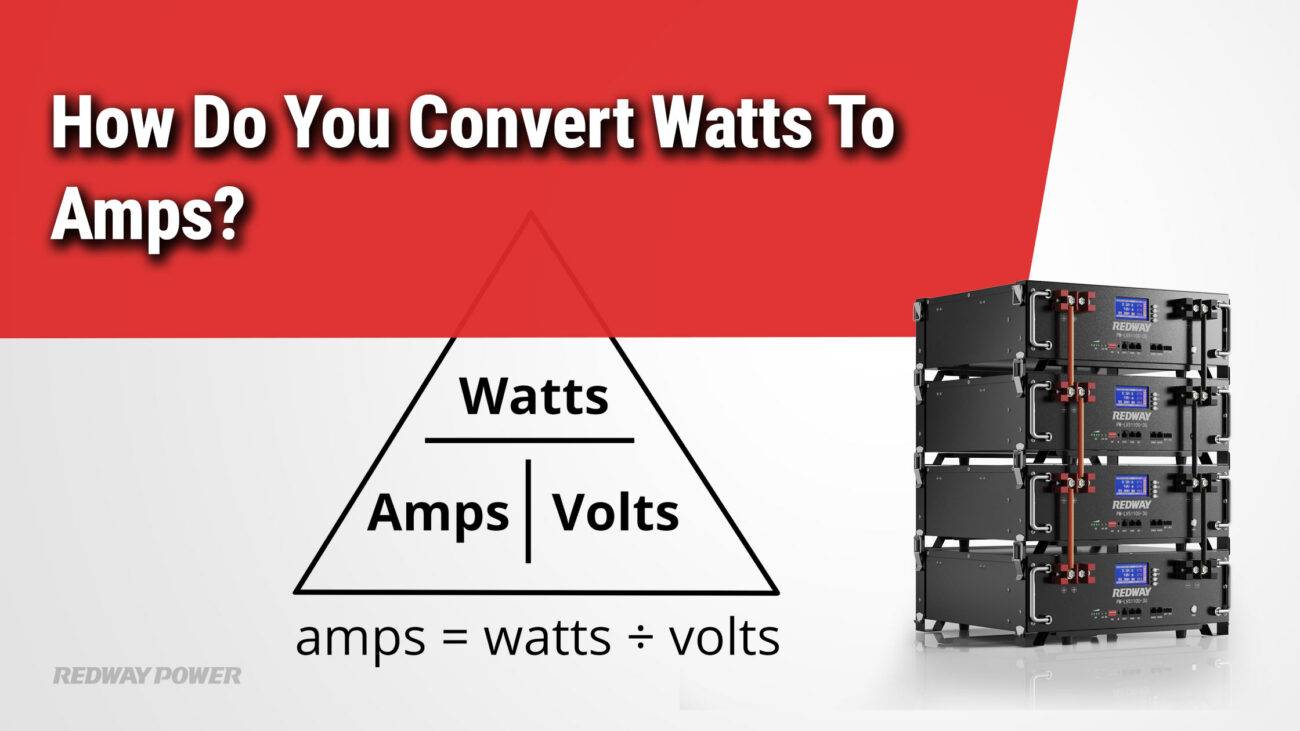
How Do You Calculate Watts from Amps and Voltage?
To find watts, multiply the current by the voltage:
Watts=Amps×Volts
For example, if a device draws 5 amps at 12 volts, the power is:
5 A×12 V=60 W
This formula is the foundation for understanding power consumption and sizing electrical components correctly.
Which Factors Affect the Relationship Between Watts and Amps?
The relationship varies with voltage levels and whether the current is direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). For AC circuits, power factor (PF)—which accounts for phase difference between voltage and current—may affect real power calculations:
Watts=Amps×Volts×Power Factor
In purely resistive AC loads, PF=1, making watts equal to volts times amps. In inductive or capacitive loads, PF < 1, reducing actual power.
When Should You Use the Watts-Amps Formula?
Use this formula to determine electrical power consumption, ensure compatibility of electrical systems, calculate energy requirements, or select cables and circuit breakers. It’s key in contexts such as solar power setups, battery systems, home electrical wiring, and vehicle electronics.
Can You Convert Amps to Watts Without Voltage?
No, you cannot determine watts from amps alone since watts depend on volts as well. Knowing the voltage is essential. For example, 10 amps at 12 volts is 120 watts, but 10 amps at 120 volts is 1200 watts, a tenfold difference.
How Does Redway Power Relate to Watts and Amps in Battery Pack Manufacturing?
Redway Power’s expertise in lithium battery pack OEM production involves precise engineering around watts and amps to ensure optimal power delivery and safety. Understanding the voltage and current demands of forklifts, golf carts, and other applications allows Redway Power to tailor battery packs that deliver reliable wattage output at correct amperage, optimizing performance and longevity.
What Are Practical Examples of Watt and Amp Relationships?
| Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (Watts) |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 10 | 120 |
| 24 | 15 | 360 |
| 48 | 20 | 960 |
| 120 | 5 | 600 |
| 240 | 10 | 2400 |
This chart illustrates how wattage varies directly with both amps and volts.
How Do Power Factor and Circuit Type Influence Watt-Amps Calculations?
In AC circuits, the power factor adjusts the “real” power consumed:
- Resistive loads (heaters, incandescent bulbs): PF ≈ 1, thus Watts = Volts × Amps.
- Inductive loads (motors, transformers): PF < 1, meaning actual watts are less than volts × amps.
- Capacitive loads behave similarly in PF impact.
For DC circuits, PF is always 1, so watts are the direct product of volts and amps.
Why Is It Important to Understand Watts and Amps in Electrical Systems?
Understanding these units helps in safely designing electrical circuits, sizing batteries, selecting proper fuses, and ensuring devices operate within power ratings. It prevents overloads, optimizes efficiency, and maximizes equipment lifespan.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Grasping the interplay between watts and amps is fundamental in battery manufacturing and electrical design. At Redway Power, our 13 years in OEM lithium battery production hinge on accurate calculations of current and voltage to tailor power delivery precisely for applications like forklifts, golf carts, and solar systems. This ensures safety, reliability, and peak efficiency in every pack we produce.” — Redway Power Expert
Conclusion
An amp measures electric current, while watts measure power—determined by multiplying amps by volts. You cannot convert amps to watts without knowing the voltage, and in AC circuits, power factor often plays a role. Understanding this relationship is key in electrical system design, battery manufacturing, and ensuring operational safety and efficiency. Trusted industry experts like Redway Power utilize these principles to produce optimized, high-performance lithium battery packs suited for a variety of applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How many watts equal one amp?
A: It depends on the voltage. Watts = Amps × Volts. For example, 1 amp at 120 volts equals 120 watts.
Q: Can I convert amps to watts without knowing voltage?
A: No, voltage is necessary to calculate watts from amps.
Q: Does power factor affect watts conversion in AC circuits?
A: Yes, power factor adjusts the real power value, especially in inductive or capacitive loads.
Q: What is the typical power factor value?
A: It ranges from 0 to 1, commonly about 0.8 to 1 for many residential loads.
Q: How does Redway Power ensure proper current and power in battery packs?
A: Redway Power uses precise calculations of amps and volts to engineer lithium battery packs for optimal energy delivery and safety.