Understanding the differences between lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries is essential when choosing the right battery technology. As an expert in lithium battery manufacturing, we highlight the distinct advantages of lithium-ion batteries.
What is lead acid batteries?
Lead acid batteries are rechargeable batteries that use lead and sulfuric acid to generate electricity. They consist of lead plates immersed in sulfuric acid, facilitating a controlled chemical reaction to produce electrical energy. Lead acid batteries are commonly used in automotive, industrial, and backup power applications due to their reliability and relatively low cost.
What is lithium ion batteries?

Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that utilize lithium ions to store and release energy. They are composed of positive and negative electrodes made of lithium-containing materials, separated by an electrolyte. Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and ability to provide long-lasting power, making them popular for applications such as portable electronics, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems.
Lead-acid vs Lithium-ion Batteries
When it comes to selecting the right battery technology, understanding the key differences between lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries is crucial. As an expert in lithium battery technology, I’ll outline the distinct advantages of lithium-ion batteries over lead-acid alternatives.
Weight Advantage
Lithium-ion batteries weigh significantly less than lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as in portable devices or electric vehicles.
Extended Cycle Life
Lithium-ion batteries boast impressive cycle lives ranging from 1,000 to 20,000 cycles, far surpassing the longevity of lead-acid batteries. This extended lifespan translates to reduced maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Cost Efficiency Over Time
While lithium-ion batteries may have a higher upfront cost, their superior durability and efficiency result in lower long-term operating costs and a higher return on investment compared to lead-acid batteries.
Enhanced Capacity and Efficiency
With higher energy density, lithium-ion batteries can store more energy in a smaller space, enabling increased capacity and prolonged runtime. Additionally, their high efficiency ensures minimal energy loss during charge and discharge cycles.
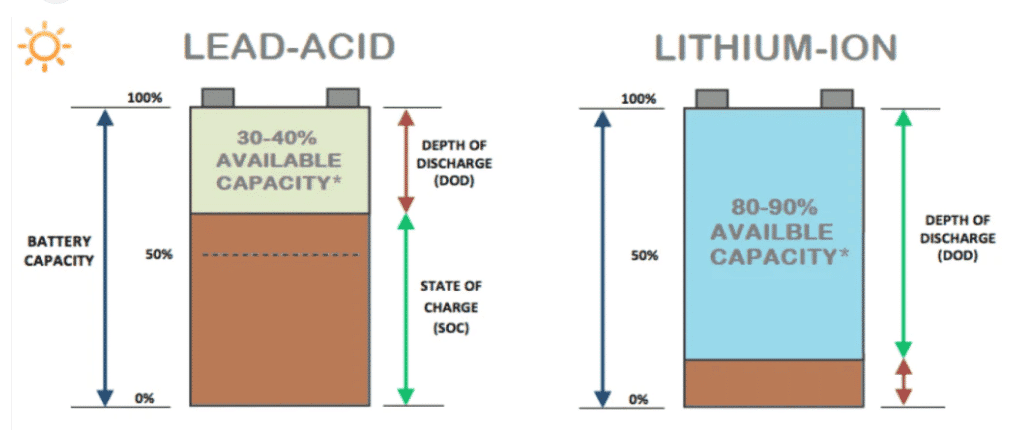
Superior Performance in Various Conditions
Lithium-ion batteries outperform lead-acid batteries in challenging environments, maintaining efficiency and cycle life even under extreme temperatures or frequent charging cycles.
Rapid Charging Capabilities
Lithium-ion batteries offer significantly faster charging times compared to lead-acid batteries, reducing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency. This rapid charging capability ensures swift turnaround times, enhancing productivity in various applications.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries emerge as the clear choice for modern energy storage needs, offering unparalleled performance, longevity, and efficiency compared to lead-acid alternatives.
FAQs
Which is better? Lithium vs lead acid battery
Lithium-ion batteries are generally considered better than lead-acid batteries due to their higher energy density, longer lifespan, faster charging capabilities, and lower maintenance requirements.
How much longer do lithium batteries last compared to lead acid?
Lithium-ion batteries typically last significantly longer than lead-acid batteries. While lead-acid batteries may have a lifespan of around 500 cycles, lithium-ion batteries can last anywhere from 1,000 to 20,000 cycles, depending on the specific chemistry and usage conditions.
How long does it take to charge lithium-ion vs lead acid?
Lithium-ion batteries generally charge much faster than lead-acid batteries. While the charging time can vary depending on factors such as battery capacity and charging method, lithium-ion batteries typically charge in a fraction of the time it takes to charge lead-acid batteries.
Is it safe to replace lead acid battery with lithium-ion?
It can be safe to replace a lead-acid battery with a lithium-ion battery, but it’s essential to ensure compatibility with the device or system. Proper installation and consideration of voltage and charging requirements are crucial to prevent damage or safety hazards.
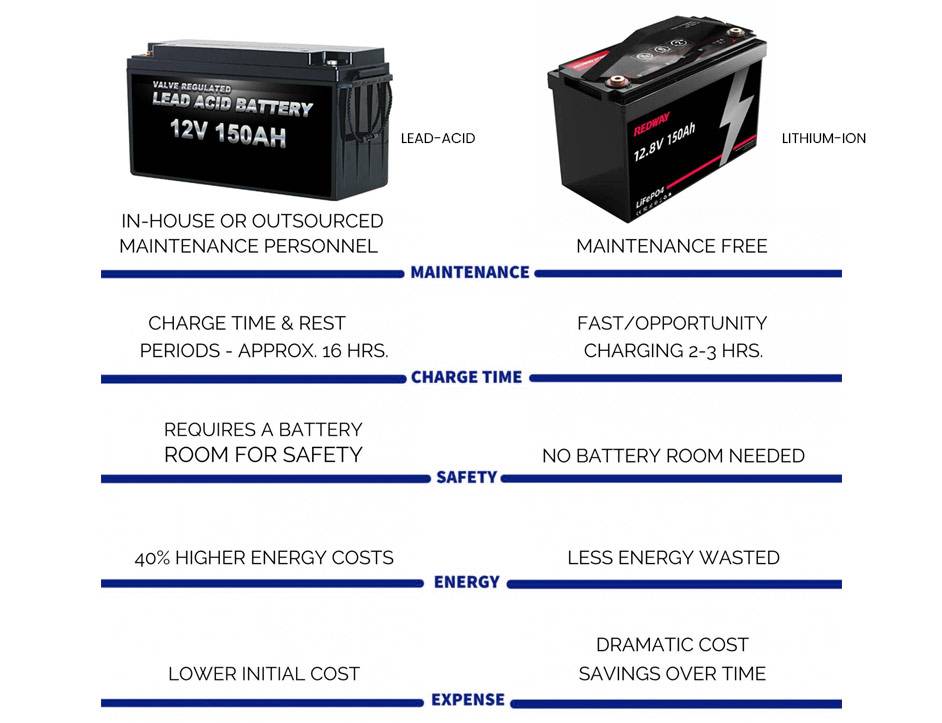
What happens if you charge a lead-acid battery too fast?
Charging a lead-acid battery too quickly can lead to overheating, excessive gassing, and potentially damage to the battery. It can also reduce the battery’s lifespan and compromise its performance and safety.
How many times can a lead-acid battery be recharged?
Lead-acid batteries typically have a limited number of charge cycles, usually around 300 to 500 cycles, before their capacity and performance start to degrade significantly.
What shortens the life of lithium batteries?
Several factors can shorten the life of lithium-ion batteries, including high temperatures, overcharging, deep discharges, physical damage, and poor battery management practices.
Which battery has the longest lifespan?
Among lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion batteries generally have the longest lifespan. Depending on the specific chemistry and usage conditions, lithium-ion batteries can last significantly longer, with some types capable of enduring tens of thousands of charge cycles.
Why make the switch to lithium batteries?
As an expert in lithium battery technology, I’ll outline the distinct advantages of lithium-ion batteries over lead-acid alternatives. Lithium-ion batteries emerge as the clear choice for modern energy storage needs, offering unparalleled performance, longevity, and efficiency compared to lead-acid alternatives. Lithium-ion batteries excel in various aspects, including their lightweight nature, delivering up to 50% more energy while weighing one-third less than traditional lead-acid batteries. Moreover, their high efficiency, with super-low resistance resulting in 99% efficiency, enables rapid charging with minimal energy loss, a significant advantage over lead-acid counterparts that experience power depletion during discharge. Additionally, lithium batteries provide 100% of their rated capacity regardless of discharge rate, ensuring consistent energy output, unlike lead-acid batteries that limit usable energy at higher discharge rates to prevent premature deterioration. Furthermore, the ultra-long life of lithium batteries, capable of cycling 3,500 times or more with minimal impact from discharge levels, far surpasses the longevity of lead-acid batteries that typically offer only 300-500 cycles. These features collectively make lithium batteries the optimal choice for those seeking reliable, efficient, and long-lasting energy storage solutions.





