Blog
Watts, Volts, Amps, and Ohms: What are the Differences

Watts measure the electrical power used or produced by a device, volts indicate the electric pressure pushing current through a circuit, amps quantify the flow rate of electric current, and ohms signify the resistance opposing this flow. Understanding these units helps optimize battery and electrical device performance safely and efficiently.
What Are Watts, Volts, Amps, and Ohms?
Watts (W) represent the total power in an electrical system, calculated by multiplying volts and amps. Volts (V) are the electrical potential or pressure that pushes electrons through a conductor. Amps (A), short for amperes, measure the quantity or flow rate of electrons passing a point in the circuit. Ohms (Ω) measure electrical resistance, indicating how much a material opposes the flow of current.
How Do Watts, Volts, Amps, and Ohms Relate to Each Other?
These units are intricately linked by Ohm’s Law and power formulas. Watts equal volts times amps (W = V × A), showing power as a product of pressure and current. Amps equal volts divided by ohms (A = V ÷ Ω), explaining how current flow depends on voltage and resistance. Resistance affects how easily current flows, influencing power consumption and device operation.
What Is Voltage and How Does It Work?
Voltage is the force or electric pressure that pushes electrons through a circuit, similar to water pressure in a pipe. It determines how much potential energy per unit charge is available to move electric current. Higher voltage means a greater ability to do work, powering devices more forcefully or over longer distances.
What Are Amps and What Do They Measure?
Amperage measures the volume or quantity of electrons flowing through a circuit per second. It reflects how much electrical charge is moving and is essential to understanding circuit capacity and device energy consumption. Higher amps signify a stronger electrical current capable of powering more demanding equipment.
What Is a Watt and How Is It Calculated?
A watt measures electrical power, indicating the rate at which energy is used or produced. It is calculated by multiplying voltage by current (W = V × A). For example, a device running at 120 volts drawing 10 amps consumes 1200 watts of power. Watts help assess energy efficiency and sizing of electrical components.
[Chart title: Relationship Between Watts, Volts, and Amps]
What Is Ohm and Why Is Resistance Important?
Ohms quantify resistance, showing how much a material restricts the flow of electric current. Resistance converts some electrical energy into heat, reducing current flow and affecting circuit performance. Managing resistance is crucial in battery design and electrical systems to optimize efficiency and safety.
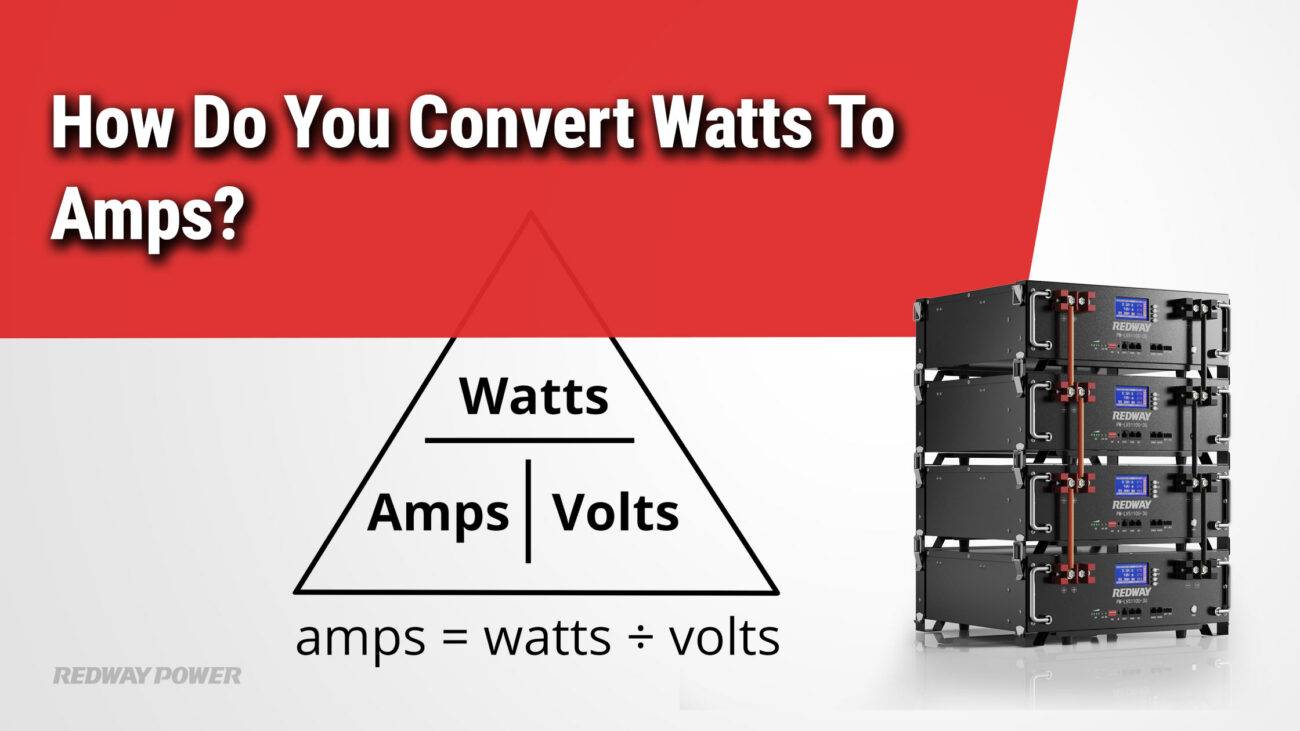
How Do You Calculate Watts, Volts, Amps, and Ohms in Electrical Circuits?
Using Ohm’s Law and power formulas, electrical calculations can identify voltage, current, power, or resistance. For instance:
- Amps = Volts ÷ Ohms (A = V ÷ Ω)
- Watts = Volts × Amps (W = V × A)
- Resistance = Volts ÷ Amps (Ω = V ÷ A)
These formulas assist technicians and engineers in analyzing and designing electrical systems accurately.
How Do These Units Impact Battery and Electrical Device Performance?
In battery systems, voltage determines how much force drives current, amps show how much current flows, watts indicate total power delivery, and ohms affect energy loss through resistance. High-performance lithium batteries, like those from Redway Power, optimize these parameters with advanced design, enabling longer runtimes and efficient energy use.
What Are Common Misconceptions About Watts, Volts, Amps, and Ohms?
A frequent misunderstanding is confusing volts with amps, or watts with voltage alone. Volts alone do not measure energy consumption; amps and volts together determine watts (power). Another misconception is that higher voltage always means higher power; without sufficient current, power remains limited, underscoring the need to consider all units jointly.
How Are These Electrical Principles Applied in Real-World Battery Systems?
Battery manufacturers apply these principles to balance voltage, current, resistance, and power to meet application needs. Redway Power’s lithium battery packs use precise engineering to optimize Ohm’s Law parameters for industrial, telecom, and electric vehicle uses. Accurate control of these factors leads to safer, more durable, and efficient battery systems.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding how watts, volts, amps, and ohms interplay is essential for designing robust battery systems,” says a Redway Power electrical engineer. “Our OEM lithium batteries are crafted to precisely balance these elements using advanced Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), ensuring performance, reliability, and safety. Mastery of these principles empowers engineers and users to harness electrical power effectively.”
Conclusion
Watts, volts, amps, and ohms are fundamental electrical units describing power, pressure, current, and resistance in circuits. Their interrelationship defines how electrical devices and batteries function through Ohm’s Law and power calculations. Grasping these differences is key to optimizing energy use and ensuring safe, efficient operation, exemplified by Redway Power’s expertly engineered lithium battery solutions.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between volts and amps?
A: Volts measure the electrical pressure, while amps measure the flow of electrical current.
Q: How do watts relate to volts and amps?
A: Watts equal volts multiplied by amps and represent the total electrical power.
Q: Why is resistance measured in ohms important?
A: Resistance controls current flow and affects how efficiently a circuit operates.
Q: Can I calculate volts, amps, watts, or ohms using formulas?
A: Yes, Ohm’s Law and power formulas let you calculate any of these values if others are known.
Q: How does Redway Power ensure quality battery performance?
A: Redway Power integrates expert design and MES to optimize electrical parameters for durable, efficient batteries.